OpenAI Hires OpenClaw Founder Peter Steinberger to Drive Next-Generation AI Agents
OpenAI has officially secured a high-profile hire in Peter Steinberger, creator of the open-source AI agent OpenClaw, as part of its strategic push to build the future of autonomous personal agents — a major shift for AI companies racing to redefine what intelligent systems can do for users. Steinberger, revered for engineering one of the most popular independent AI agent frameworks, will now help OpenAI accelerate its multi-agent and autonomous AI ambitions, integrating advanced agent capabilities into its broader product ecosystem. Why this matters now: With agents moving from experimental tools to mainstream utilities, this move boosts OpenAI’s competitive edge while promising a new era of AI systems that don’t just respond — they act on behalf of people.
Visionary Hire Strengthens OpenAI’s AI Agent Strategy
Peter Steinberger’s decision to join OpenAI marks a significant moment in the evolution of autonomous AI systems. Originally developed under names like Clawdbot and Moltbot before becoming OpenClaw, his open-source agent framework quickly captured developer interest due to its ability to execute tasks across messaging platforms such as WhatsApp, Telegram, and Slack — going beyond simple chat responses to perform real actions like managing calendars or checking flights.
Sam Altman, CEO of OpenAI, described Steinberger as “a genius with a lot of amazing ideas about the future of very smart agents interacting with each other to do very useful things for people,” underscoring how these capabilities could become core to the next generation of AI products. This hire isn’t just about talent — it signals OpenAI’s commitment to shaping how AI assistants will increasingly work collaboratively and autonomously in daily life.
What OpenClaw Brought to the AI World
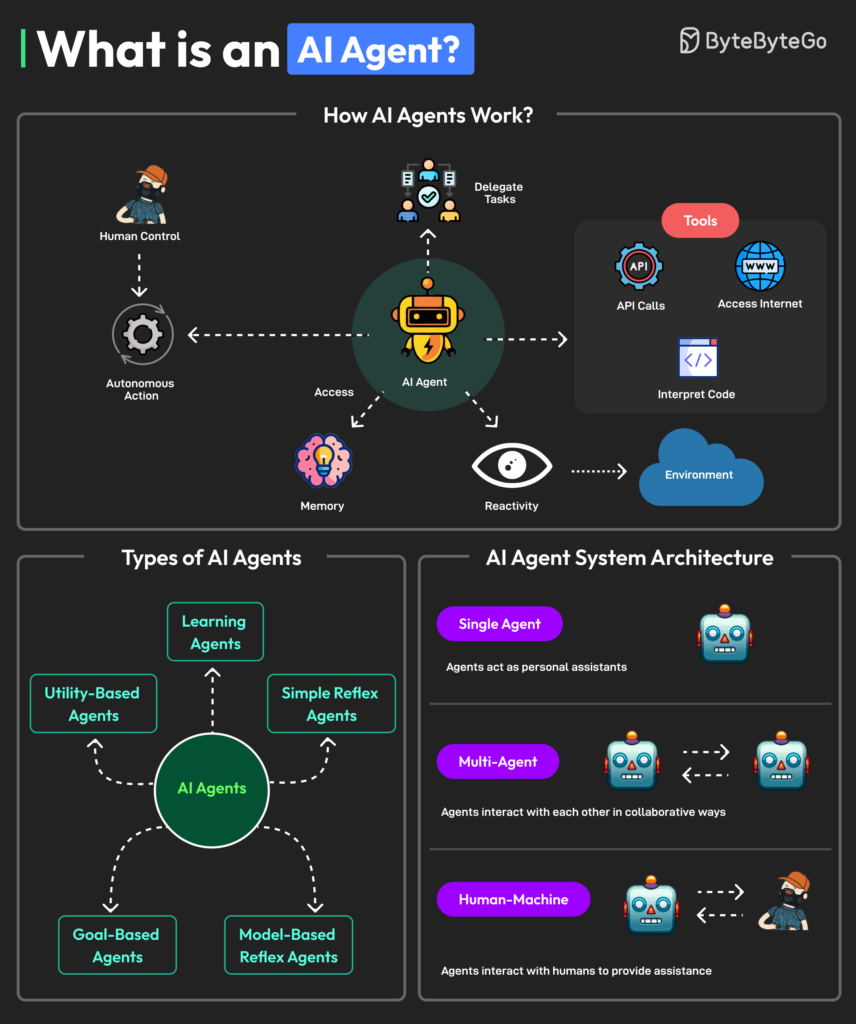
OpenClaw quickly became a viral phenomenon in late 2025 and early 2026 after its release on GitHub as a free and open-source autonomous agent platform. It amassed substantial community support, earning tens of thousands of stars and forks as developers experimented with its integration to build real-world workflows. Because it could operate locally on user devices and leverage powerful language models to make decisions, OpenClaw stood out as a leading example of what personal AI assistants could achieve outside traditional apps.
Perhaps as importantly, the project showed what next-generation agents look like — systems capable of acting as digital teammates rather than passive tools. This broader shift towards agent-based computing is already reshaping expectations for AI, and OpenClaw’s popularity and flexibility helped put that transition center stage.
OpenClaw Remains Open Source Under a New Foundation
Despite joining OpenAI, Steinberger has emphasized that OpenClaw itself will not disappear or be absorbed into proprietary systems. Instead, the project will transition into an independent foundation and continue as an open-source initiative supported by OpenAI. This structure aims to preserve community involvement while enabling Steinberger to apply his expertise to larger mainstream platforms with greater resources and reach.
By keeping OpenClaw open and independent, OpenAI signals its support for collaborative innovation — a key ethos within the AI community that fosters experimentation and access rather than restricting development behind closed doors. For many developers and users, this balance may determine how quickly agent-based tools evolve from niche tech into everyday utilities.

Why This Matters to the AI Industry Today
This hire comes at a time when multiple AI developers are competing to define the next frontier of intelligent systems. Personal agents that can perform complex, multi-step tasks autonomously — such as planning trips, managing communications, or performing research — are seen as a major step beyond current AI chatbots. OpenAI’s acquisition of Steinberger’s talent places it strategically ahead in this race.
Investors and analysts view such moves as a sign that the industry is pivoting toward action-oriented AI systems that don’t just answer queries, but execute workflows with minimal user input. With competitors like Anthropic and Google advancing their own efforts, integrating agent-centric talent like Steinberger’s may accelerate innovation across the board.
Potential Risks and the Path Forward
Despite the excitement, agent technologies also raise fresh concerns around security, privacy, and control. Because these systems often require deep access to user data and services to act autonomously, experts have warned that inadequate safeguards could expose vulnerabilities if misconfigured or exploited. Independent research highlights that these agents demand careful development practices and strong protections to prevent misuse.
OpenAI and Steinberger will need to address these issues as part of broader adoption efforts — especially as such tools move from developer labs into consumer-facing products. Success here could redefine AI’s role in productivity, accessibility, and automation.
The Future of Autonomous Personal AI Agents
Peter Steinberger’s move could accelerate the journey from prototype agents to widely used digital assistants capable of integrating into daily life. By contributing his deep expertise to OpenAI’s ecosystem, he strengthens the firm’s ability to deliver scalable, secure, and powerful agent experiences that could shape how individuals and businesses interact with AI in the years ahead.
As the era of multi-agent systems unfolds, both developers and end users can expect a wave of new tools that blur the line between instruction and action — making AI assistants more proactive, usable, and capable than ever.
Subscribe to trusted news sites like USnewsSphere.com for continuous updates.





