Mossad: Inside Israel’s Secretive Intelligence Agency That Shaped Global Espionage has long been a subject of fascination, fear, and admiration around the world. Known officially as Mossad, Israel’s foreign intelligence service operates almost entirely in secrecy, yet its influence has repeatedly surfaced in some of the most consequential geopolitical events of the last seven decades. From high-stakes counterterrorism missions to covert intelligence gathering that altered international policy decisions, Mossad has built a reputation as one of the most effective intelligence organizations in modern history.

Unlike intelligence agencies that operate within more visible bureaucratic frameworks, Mossad functions largely beyond public scrutiny. Its operations are rarely acknowledged officially, its agents remain anonymous, and its successes often become public knowledge only years or decades later. This deliberate secrecy has made Mossad both respected and controversial, fueling debates about intelligence ethics, international law, and the balance between national security and global accountability.
This article provides a comprehensive, factual, and neutral examination of Mossad—its origins, operational philosophy, confirmed historical actions, controversies, and its evolving role in the modern intelligence landscape. Rather than relying on myths or dramatized portrayals, this analysis focuses on verifiable information and contextual understanding to explain why Mossad continues to command global attention.
What Is Mossad? A Clear Explanation
Mossad is Israel’s national intelligence agency responsible for foreign intelligence collection, covert operations, and counterterrorism activities outside Israel’s borders. Its official Hebrew name translates roughly to Institute for Intelligence and Special Operations, reflecting its dual role in information gathering and clandestine action.
Despite its global reputation, Mossad operates with comparatively limited public resources. While exact figures remain classified, open-source estimates place Israel’s total annual intelligence spending between $2.5 billion and $3 billion, covering Mossad, military intelligence, and domestic security combined. Mossad itself is believed to employ between 7,000 and 10,000 personnel, including analysts, technical specialists, logistics staff, and field operatives. By comparison, the U.S. intelligence community employs over 100,000 people across 18 agencies, highlighting Mossad’s relatively small size and its emphasis on precision over scale. Analysts often note that Mossad’s influence stems less from budgetary dominance and more from long-term intelligence penetration and strategic focus.
Unlike domestic security agencies, Mossad does not operate inside Israel’s borders in routine law enforcement roles. Those responsibilities fall to other Israeli institutions. Mossad’s mandate is outward-facing, focused on identifying external threats, monitoring hostile actors, and preventing attacks against Israeli interests worldwide.
In structure and purpose, Mossad is often compared to agencies such as the CIA in the United States or MI6 in the United Kingdom. However, key differences exist. Mossad operates within a smaller national framework, which often allows faster decision-making and tighter operational secrecy. Its scope is narrower geographically but intensely focused, largely shaped by Israel’s unique security environment and regional dynamics.

| Agency | Country | Main Focus | Oversight Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mossad | Israel | Foreign intelligence | Executive |
| CIA | USA | Global intelligence | Congressional |
| MI6 | UK | Overseas intelligence | Parliamentary |
Mossad reports directly to the Prime Minister of Israel, which places it close to political leadership and strategic decision-making. This proximity has enabled swift authorization of operations but has also raised concerns about oversight and accountability—an issue frequently debated by scholars and international observers.
Historical Origins and Formation
The origins of Mossad are inseparable from the founding of the State of Israel in 1948. In its early years, Israel faced immediate existential threats from neighboring states, regional instability, and ongoing conflicts that made intelligence gathering a national priority. The newly established country lacked the intelligence infrastructure of older nations and had to build capabilities rapidly.
Before Mossad’s formal establishment, intelligence activities were carried out by fragmented units tied to military and political organizations. These efforts, while effective in certain cases, lacked centralized coordination. Recognizing the need for a unified foreign intelligence body, Israeli leadership moved to consolidate intelligence operations under a single institution.
Mossad was officially established in 1949, initially focusing on gathering intelligence about neighboring states and monitoring military threats. During its formative years, the agency relied heavily on human intelligence networks, particularly among Jewish communities abroad and regional contacts. These early networks became the foundation for Mossad’s later global reach.

The Cold War period significantly shaped Mossad’s evolution. As global intelligence competition intensified, Mossad expanded its capabilities, modernized its methods, and developed long-term intelligence assets across multiple continents. Cooperation with Western intelligence agencies increased, particularly in areas of shared security interests, while operational independence remained a defining feature.
How Mossad Operates: Methods and Philosophy
Mossad’s operational philosophy emphasizes precision, long-term planning, and deniability. Rather than relying on large-scale operations, the agency focuses on carefully targeted actions designed to achieve strategic objectives with minimal exposure.

Publicly available assessments suggest that Mossad maintains intelligence assets or operational presence—direct or indirect—in more than 80 countries worldwide. Over the past two decades, Israeli officials and investigative reports have acknowledged intelligence activity spanning the Middle East, Europe, Africa, Asia, and Latin America. Between 2000 and 2024, dozens of Mossad-linked intelligence cases surfaced in international courts and media investigations, underscoring the agency’s global footprint. Security analysts emphasize that many operations involve years of intelligence groundwork, often requiring coordination across multiple jurisdictions and partner intelligence services.

One of Mossad’s core strengths lies in human intelligence (HUMINT). The agency invests heavily in recruiting and cultivating long-term assets who can provide insight into political movements, military developments, and emerging threats. These assets are often embedded over many years, allowing Mossad to build deep contextual understanding rather than relying solely on short-term information.

At a high level, Mossad also integrates signals intelligence, cyber intelligence, and analytical research. However, unlike technical intelligence agencies that prioritize mass data collection, Mossad is known for selective intelligence gathering, focusing on actionable insights rather than volume.
Recruitment within Mossad is highly selective. Candidates undergo extensive psychological evaluation, language training, and operational preparation. Emphasis is placed on adaptability, cultural awareness, and discretion. Agents are trained to operate independently under extreme pressure, often without immediate support.
Operational secrecy is maintained through strict compartmentalization. Information is shared only on a need-to-know basis, reducing the risk of exposure. This structure has allowed Mossad to conduct operations across multiple jurisdictions while limiting diplomatic fallout when activities become public.
Famous Confirmed Operations and Their Global Impact
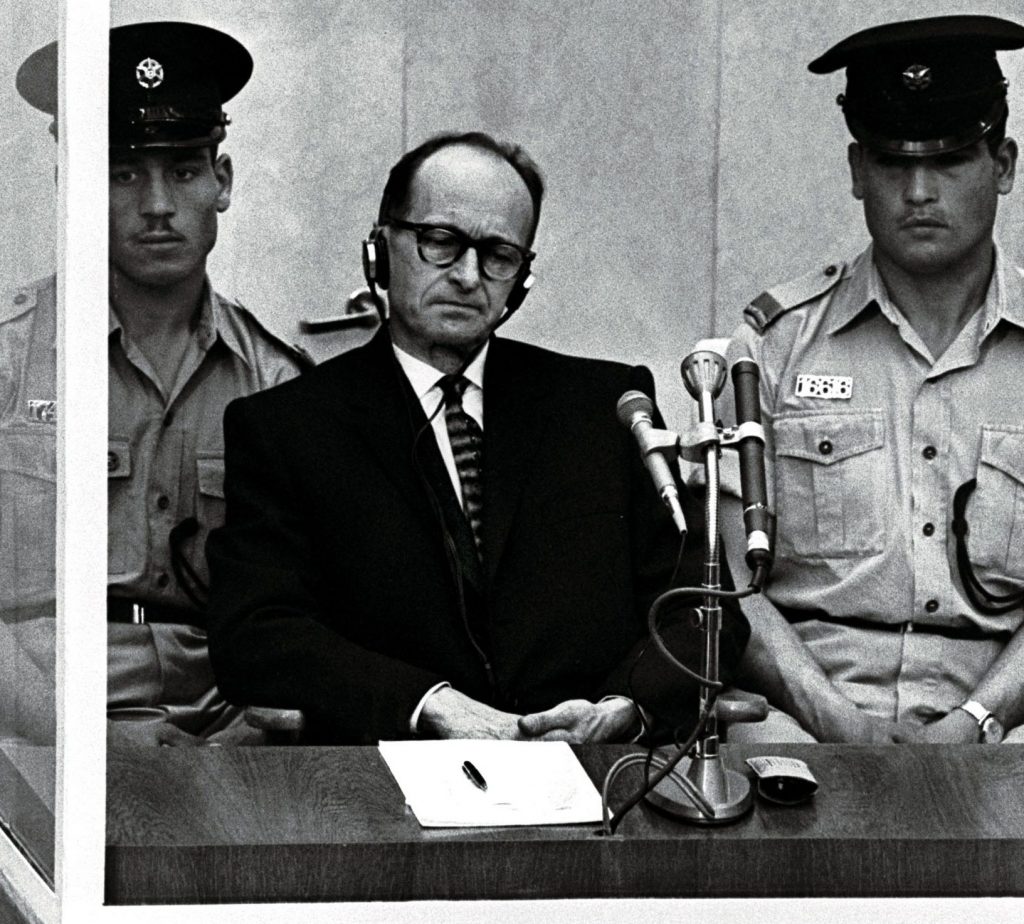
Several Mossad operations have entered the public record due to their historical significance and long-term consequences. One of the most widely documented cases is the capture of Adolf Eichmann, a key architect of the Holocaust, who was located in Argentina in 1960. The operation resulted in Eichmann being brought to Israel to stand trial, marking one of the most significant post-war justice actions against Nazi war criminals.

Israeli security assessments indicate that intelligence-led prevention has played a central role in national security outcomes. According to official statements released over the years, Israeli intelligence agencies collectively have disrupted hundreds of planned attacks since the early 2000s, many of them outside Israel’s borders. While Mossad rarely claims operational credit, its foreign intelligence role is widely acknowledged in cases involving overseas terror financing, weapons transfers, and leadership tracking. Between 2010 and 2023, Israeli officials publicly credited intelligence cooperation—including Mossad involvement—for helping prevent attacks targeting diplomatic missions, aviation routes, and civilian populations in multiple countries.

Here are some of the Mossad’s famous confirmed operations:
- Operation Finale (Capture of Adolf Eichmann (1960))
- Operation Entebbe (Response to the 1972 Munich Olympics massacre)
- Operation Wrath of God (Hostage rescue in Uganda, 1976)
- Operation Brothers (Defection of Iraqi MiG-21 pilot (1966))
- Operation Diamond (Secret rescue of Ethiopian Jews via Sudan)
- Operation Orchard (Intelligence groundwork before Iraq nuclear strike (1981))
- Operation Opera (Uranium acquisition operation (1960s))
- Operation Damocles (Targeting Nazi scientists working in Egypt)
- Operation Plumbat (Syrian nuclear reactor intelligence, 2007))
- Operation Bayonet (Targeted intelligence actions tied to terrorism prevention)
- Operation Sphinx (Intelligence operations targeting Libyan weapons programs)
- Operation Noah’s Ark (Early Jewish rescue and relocation intelligence efforts)
- Operation NTFV (Operation Babylon – Intelligence Phase) (Intelligence groundwork around Iraq’s nuclear ambitions)
- Operation Zefira (Intelligence penetration into hostile political networks)
- Operation Athena (European counterterror intelligence cooperation missions)
- Operation Kidon (Unit-Linked Missions) (Assassination-focused intelligence unit operations (publicly acknowledged existence, not details))
- Operation Spring of Youth (Intelligence Support Phase) (Intelligence planning behind Beirut operations (1973))
- Operation Quiet Valley (Intelligence surveillance operations in hostile regions)
- Operation Yachin (Intelligence role in Moroccan Jewish migration)
- Operation Nikkah (Counterintelligence monitoring of extremist networks)

One of Mossad’s most documented long-term priorities has been monitoring weapons proliferation. Open-source intelligence analyses show that Israeli intelligence efforts related to nuclear monitoring span more than four decades, intensifying significantly after the early 2000s. During this period, international agencies conducted hundreds of inspections, while intelligence assessments repeatedly influenced diplomatic negotiations, sanctions regimes, and security planning. Analysts note that intelligence reporting—rather than military action—has often been the primary driver shaping international responses to suspected nuclear development programs in the Middle East.
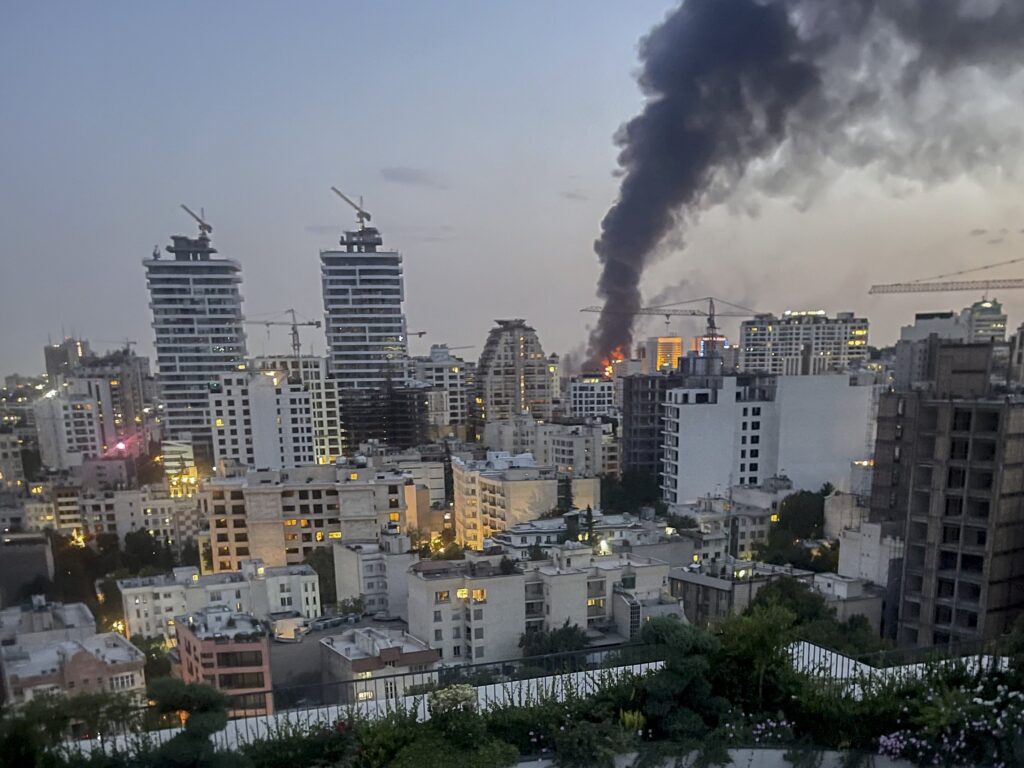

Recent Mossad-Linked Operations (2023–2026):
- Operation Rising Lion (A major coordinated mission combining Mossad’s covert sabotage inside Iran with large-scale Israeli strikes on Iranian missile and nuclear infrastructure.)
- Mossad Covert Drone & Sabotage Operations in Iran (Mossad agents reportedly smuggled and used explosive drones and advanced systems inside Iran to disable air defenses and launchers ahead of the June 2025 offensive.)
- Deployment of Mossad Operatives Inside Iran (Reports indicate Mossad deployed around 100 agents in Iran to install and operate systems that helped neutralize missile launchers and defenses.)
- Targeting of Iranian Nuclear Scientists & Commanders (Officials briefed reporters that Mossad helped locate and target key nuclear scientists and commanders during the June campaign, contributing to their elimination.)
- Reported Mossad Involvement in Iranian Internal Unrest (Iranian authorities have accused Mossad of influencing or exploiting nationwide protests and unrest, claiming intelligence interference during major demonstrations.)
- Arrests of Alleged Mossad Operatives in Iran (Iranian police and state media have reported detaining individuals accused of working with Mossad during periods of civil unrest and espionage cases.)
- Execution of Convicted Mossad Spy in Iran (Iran executed a man it convicted of acting on behalf of Mossad by providing sensitive strategic information, according to state media reports.)
- Mossad Named Suspect in Disrupting Hezbollah Supply Tools (Many analysts connected Mossad-style tactics to the 2024 Lebanon electronic device attacks that targeted Hezbollah communications gear (commonly reported in media as part of Israeli intelligence silencing Hezbollah networks).)
- Increased Mossad Intelligence Focus on Nuclear and Missile Programs (Media investigations and reports showed continuous Mossad ground intelligence on Iranian nuclear sites for many years, leading up to and during escalations.)
- Identification of Threat Actors Linked to Attacks on Jewish Communities (In international news outlets, Mossad publicly identified operatives linked to attacks on Jewish institutions abroad, prompting diplomatic actions by other governments.)

Beyond historical justice, Mossad has been involved in numerous counterterrorism efforts aimed at preventing attacks on Israeli civilians and diplomatic missions abroad. These operations often involved intelligence-led disruption rather than direct confrontation, highlighting the agency’s preference for prevention over retaliation.
Mossad has also played a role in intelligence efforts related to weapons proliferation. Public reports indicate involvement in monitoring nuclear development programs in the Middle East, providing intelligence that influenced international policy discussions and sanctions regimes.

Each confirmed operation reflects a broader strategic objective rather than an isolated tactical success. The outcomes have often reshaped diplomatic relationships, influenced international security cooperation, and contributed to Mossad’s reputation for effectiveness.
Mossad Compared to Other Intelligence Agencies
When compared to major intelligence agencies such as the CIA or MI6, Mossad stands out for its scale and focus. Operating within a smaller national system, Mossad can act with agility and speed that larger bureaucracies sometimes lack.
While agencies like the CIA manage global intelligence responsibilities across multiple regions and domains, Mossad concentrates on specific threat environments, primarily related to Middle Eastern security and global terrorism. This focused mandate allows deeper specialization but also places intense pressure on accuracy and operational success.
Another distinguishing factor is oversight. Different democratic systems impose varying degrees of legislative and judicial review. Mossad’s oversight mechanisms exist but are less visible publicly, contributing to ongoing debates about transparency versus operational necessity.
Controversies and Criticism
Mossad’s secrecy and operational reach have inevitably generated controversy. Critics argue that certain operations have raised questions about violations of international law, sovereignty, and diplomatic norms. Allegations of unauthorized actions in foreign countries have occasionally strained Israel’s relations with allies and neutral states.
Unlike many public institutions, intelligence agencies operate under extreme secrecy. In Israel, only a small number of senior government officials and parliamentary oversight members are formally briefed on Mossad activities each year. Historically, fewer than 5–10 percent of major intelligence operations ever become publicly acknowledged, often decades later through declassified documents or investigative reporting. Scholars of intelligence governance note that this level of opacity is consistent across major intelligence agencies worldwide, reflecting the tension between democratic oversight and operational security.
Human rights organizations have also questioned the ethical implications of targeted operations, emphasizing the need for accountability and adherence to international standards. Supporters counter that intelligence agencies operate in morally complex environments where conventional legal frameworks may not adequately address security threats.
These debates are not unique to Mossad but reflect broader global discussions about intelligence practices in an era of asymmetric warfare and transnational terrorism.
Mossad in the Modern World (2020–2025)
In recent years, Mossad has adapted to a rapidly changing intelligence environment. Cyber threats, digital surveillance, and artificial intelligence have transformed how intelligence is collected and analyzed. Mossad has reportedly invested heavily in technological innovation while maintaining its traditional emphasis on human intelligence.
The rise of non-state actors, cyber warfare, and decentralized extremist networks has expanded the scope of intelligence challenges. Mossad’s role has increasingly involved early threat detection and international intelligence cooperation, particularly with Western and regional partners.
Modern operations emphasize prevention, strategic foresight, and intelligence diplomacy, reflecting a shift from reactive responses to proactive risk management.
Public Perception and Cultural Impact
Mossad’s mystique has inspired books, documentaries, and fictional portrayals that often blur the line between fact and imagination. While popular culture tends to dramatize intelligence work, these portrayals have contributed to Mossad’s global reputation as a highly capable and disciplined organization.
Public fascination persists largely because verified information remains limited. This scarcity of detail fuels speculation, reinforcing Mossad’s image as an intelligence service operating beyond conventional boundaries.
Why Mossad Still Matters
Mossad remains a central player in global intelligence not because of myths or exaggeration, but due to its consistent strategic impact over decades. Its operations have influenced regional security, international diplomacy, and global counterterrorism efforts.
Understanding Mossad requires moving beyond sensational narratives to examine the structural, historical, and ethical realities of intelligence work. In an increasingly complex and interconnected world, intelligence agencies like Mossad will continue to play critical roles—often unseen, frequently debated, and always consequential.
As global security challenges evolve, Mossad’s ability to adapt while maintaining operational secrecy will determine its influence in the decades ahead.
Subscribe to trusted news sites like USnewsSphere.com for continuous updates.





