This Flu Season Surge 2026 is unlike anything most Americans have experienced in years, with respiratory illnesses rising to historically high levels, overwhelming hospitals, and even causing tragic deaths among children and adults. Across the United States, health authorities and experts are sounding the alarm that this year’s influenza activity is not only widespread but also striking earlier and harder than many anticipated.
Why the 2025–26 Flu Season Is Trending as One of the Worst in Years
Experts monitoring the flu this winter report that influenza activity is climbing rapidly across the United States, with outpatient visits for respiratory illnesses reaching record levels not seen in decades. Newly released surveillance reports show that the proportion of doctor visits due to flu-like symptoms is unusually high for this time of year, and hospitals in several states are reporting admissions surging beyond typical seasonal expectations.
One of the striking factors is the dominance of a particular influenza virus variant known as H3N2 subclade K. Though not necessarily more biologically severe in illness for individuals, this version of the virus spreads extremely efficiently and appears to evade some of the immune protection provided by last year’s vaccine formulation. That combination — high transmissibility and imperfect vaccine match — leads to more people getting infected, more doctor visits, and more hospitalizations than is typical for a standard flu season.
Additionally, public health experts point out that the virus may be circulating earlier than usual, shortening the preparation window and catching many communities off guard as they enter the winter months.
The Human and Healthcare Impact: From Emergency Rooms to Pediatric Cases
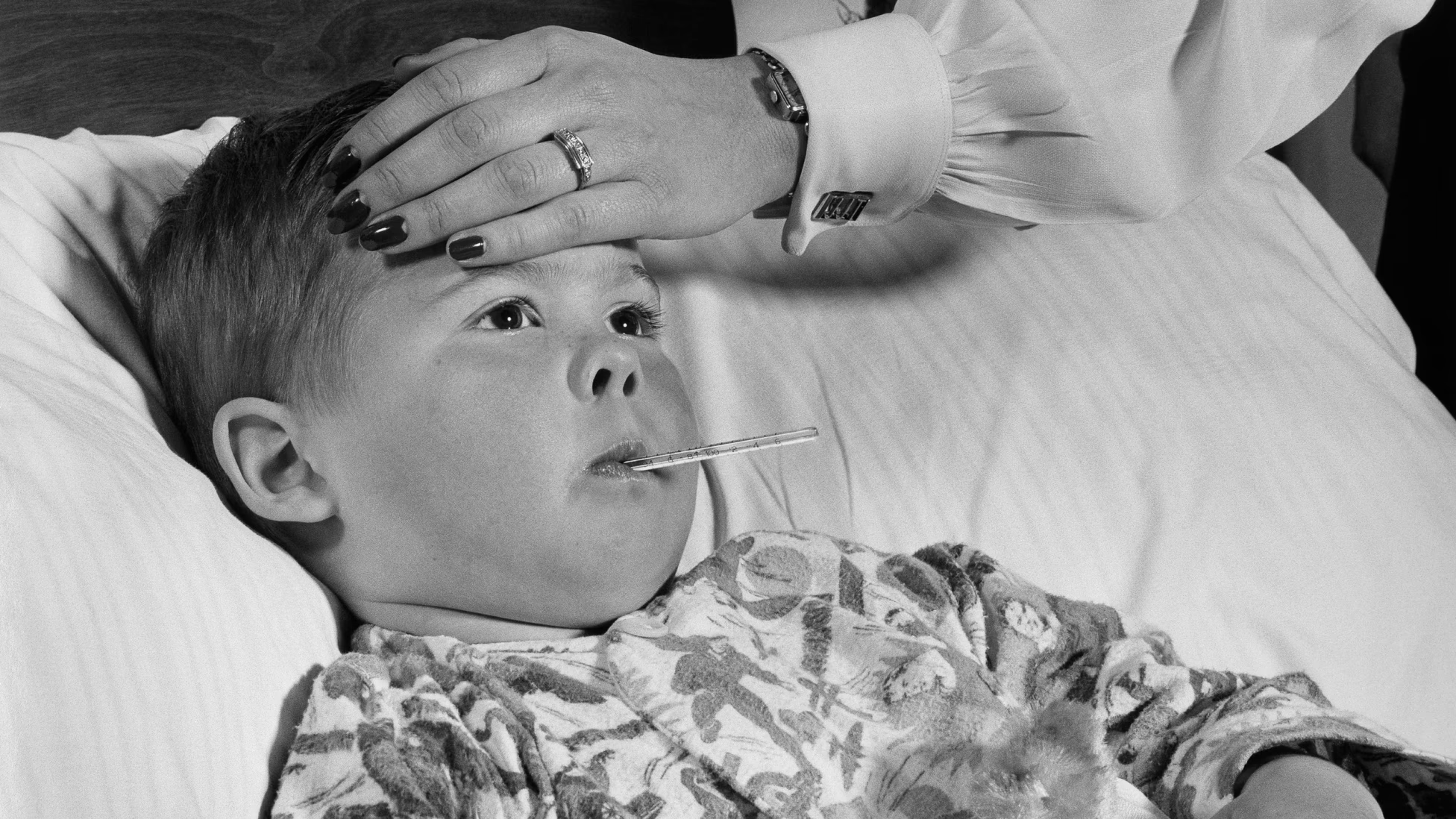
Across multiple U.S. states, emergency departments have seen an influx of influenza cases that is putting pressure on clinical resources. In states like Illinois, respiratory illness levels have reached “very high,” with significant numbers of children requiring hospitalization. Health officials there have lamented low vaccination rates and warned that children, seniors, and immunocompromised individuals are especially vulnerable this season.
Tragically, pediatric flu deaths have also been confirmed, underscoring the severity of the outbreak. In New Jersey, a two-year-old child died from influenza complications, with health authorities pointing to the ongoing spread of H3N2 as a contributing factor in increasing hospitalizations and severe outcomes among young children. Families and communities are mourning while doctors stress the importance of vaccinations and early medical care for severe symptoms.
Nationwide surveillance shows hospitalization rates climbing sharply alongside general increases in flu illness, highlighting the broader impact on public health infrastructure — from workforce shortages in hospitals to longer wait times in ERs and urgent care centers.
What the CDC Data Shows: Illness Counts, Hospitalizations, and Severity
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) continues to track flu activity through weekly reports that reveal the scale of the 2025–26 flu burden. CDC data indicate that this season’s activity is higher than average for this point in the season, and that several key flu indicators — including outpatient visits, lab-confirmed hospitalizations, and percent positivity for influenza tests — are elevated across many regions.
According to CDC estimates, cumulative influenza illnesses since the onset of the season number in the millions, with tens of thousands of hospitalizations already recorded and thousands of deaths attributed to the flu virus. These figures reflect the ongoing challenges public health officials face in keeping the outbreak contained and lessening its toll.
CDC surveillance also shows that flu activity is widespread geographically, meaning that most states and territories are reporting high levels of flu transmission, a sign that the season’s peak is well underway rather than tapering off.
Influenza Strains Explained: The Role of the Subclade K Variant
One of the defining elements of this flu season has been the prominence of the H3N2 subclade K strain, a genetic variant of the Influenza A virus. While subclade K doesn’t necessarily cause uniquely more severe symptoms at an individual level, its genetic differences make it slightly more adept at infecting people and spreading within communities compared to other strains.
Experts describe this strain as more likely to evade immune defenses because it evolved after the vaccine composition was selected earlier in the year. This mismatch means the vaccine may not perfectly align with what’s circulating, even though it still provides significant protection against severe illness, hospitalization, and death.
Globally, similar flu patterns driven by H3N2 variants have been noted in countries such as the UK, Australia, and parts of Asia and Europe, which experienced early and intense flu seasons before the U.S. outbreak began. This suggests interconnected viral spread due to global travel and makes subclade K’s prevalence a factor of international concern as well.
Vaccine Efficacy and Prevention Strategies
With the spread of influenza already in full swing, the central question for many people is: How effective is the flu vaccine against this strain, and what can I do to stay safe?
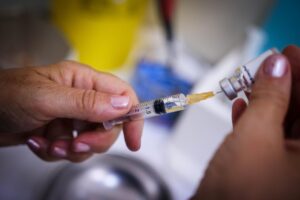
The CDC and other health authorities continue to recommend annual influenza vaccination for everyone 6 months and older, particularly for those at higher risk of complications. While vaccines may not completely prevent infection with subclade K, they still significantly reduce the chances of severe disease, hospitalization, and death — especially among children, the elderly, and individuals with chronic health conditions.
In addition, basic preventive measures such as frequent handwashing, staying home when sick, covering coughs, and wearing masks in crowded indoor settings can help diminish transmission. Hospitals in some regions have reinstated masking policies to protect staff, patients, and vulnerable populations in light of rising cases.
Public health leaders also stress the importance of early medical attention if individuals experience difficulty breathing, persistent high fever, dehydration, or neurological symptoms — signs that can indicate complications requiring urgent care.
Long-Term Implications: What This Season Tells Us About Flu Preparedness
The intensity of the 2025–26 flu season serves as a reminder of how dynamic and unpredictable influenza viruses can be. Each year, global surveillance systems and vaccine production efforts work to anticipate what strains will circulate most widely. But rapid viral evolution — as seen with subclade K — can shift these dynamics, sometimes leaving public health systems adjusting on the fly.
Experts are calling for continued investment in faster vaccine technologies, improved surveillance, and stronger public understanding of flu risks to ensure better preparedness for future seasons. Integrating these lessons with more widespread vaccination uptake could reduce the burden of future outbreaks and save lives.
In the meantime, individuals are encouraged to stay informed through trusted public health sources and to treat flu threats with the seriousness they deserve, especially in years like this one when activity is so widespread.
The 2025–26 Flu Season Is Real, Serious, and Ongoing
This 2025–26 flu season represents a significant public health challenge, marked by widespread influenza activity, early and intense transmission, and a strain that underscores the complexities of viral evolution. With millions falling ill, tens of thousands hospitalized, and parents and communities grieving losses, it is clear this flu season is unlike any in recent memory.
But there is still reason for action and hope. Vaccination remains the best defense against severe outcomes. Preventive behavior, early care, and awareness can reduce the individual and societal toll of the virus. By understanding the science, listening to health authorities, and staying vigilant, individuals can navigate this outbreak with better protection and preparedness.
Subscribe to trusted news sites like USnewsSphere.com for continuous updates.