U.S. Defense Budget 2026 stands at the center of one of the most consequential fiscal and security debates in recent years. With projections ranging between roughly $838 billion and potentially exceeding $900 billion when supplemental and emergency funding are included, the 2026 request reflects both escalating global tensions and mounting domestic budget pressure. The proposal balances troop readiness, weapons procurement, advanced technology investment, and long-term modernization — all while lawmakers grapple with rising federal deficits and growing national debt. From shipbuilding and aircraft sustainment to AI, cyber, and space capabilities, every allocation carries strategic weight. The final outcome will not only define America’s military strength in 2026 but also signal how Washington prioritizes security amid intensifying fiscal constraints.

U.S. Defense Budget 2026: What the $838–$914B Topline Means for Readiness and Procurement
The U.S. defense budget 2026, projected between $838 billion and $914 billion depending on base and supplemental funding pathways, is not just another annual spending figure — it is a direct signal of how prepared America intends to be in an era of rising global tensions. This topline number shapes everything from troop training hours and maintenance cycles to advanced weapons development and battlefield technology. At this scale, even small percentage shifts translate into tens of billions of dollars, influencing how quickly the Pentagon can modernize its forces while sustaining day-to-day readiness across the Army, Navy, Air Force, Marine Corps, and Space Force.
For readiness, the topline determines whether units are fully trained, equipment is properly maintained, and munitions stockpiles are replenished at the pace. After years of high operational tempo and global commitments, readiness funding directly affects aircraft flight hours, ship deployment cycles, spare parts inventories, and combat training rotations. If more of the budget flows toward operations and maintenance accounts, short-term military preparedness strengthens. However, if those funds tighten under fiscal pressure, service branches may face delayed maintenance, reduced training tempo, or slower replenishment of critical munitions — all factors that shape real-world military capability.
On the procurement side, the $838–$914 billion range will determine the speed of modernization programs — from next-generation aircraft and naval shipbuilding to missile defense, cyber capabilities, and space systems. Procurement funding influences how many ships are built, how quickly new fighter jets are delivered, and whether emerging technologies like AI-enabled systems move from prototype to deployment. In practical terms, this topline sets the balance between sustaining today’s force and investing in tomorrow’s battlefield advantage. The final allocation will reveal whether the United States prioritizes immediate readiness, long-term modernization, or attempts to accelerate both at once — a decision with lasting consequences for national security and global strategic balance.
How Congress Changed the DoD’s 2026 Plan: Wins, Cuts, and the Big Spending Battles
Congress did not simply approve the Pentagon’s 2026 request — it reshaped it. Lawmakers added funding to some high-priority weapons programs and munitions accounts while trimming or delaying others they viewed as costly or strategically misaligned. The final bill reflects political compromise, regional interests, and growing concern over the federal deficit.
Some of the biggest “wins” came in areas tied to readiness and industrial base strength, including shipbuilding support, missile production, and troop pay adjustments. At the same time, certain modernization programs faced scrutiny, with Congress demanding performance benchmarks, cost transparency, or schedule revisions before releasing full funding. These targeted adjustments reveal where Capitol Hill sees urgency — and where it demands accountability.
The fiercest battles centered on balancing national security priorities against fiscal pressure. With defense spending approaching historic levels, lawmakers debated whether to accelerate advanced technologies like AI and space systems or rein in growth to contain long-term debt. The outcome shows a Congress attempting to fund immediate military strength while navigating one of the most complex budget environments in decades — a tension that defines the 2026 defense debate.
Where the Money Goes: A Service-by-Service Breakdown of the 2026 Defense Budget
The 2026 defense budget is more than a single massive number — it’s a carefully divided allocation across the Army, Navy, Air Force, Marine Corps, and Space Force. Each branch receives funding based on its operational demands, modernization goals, and global commitments. Understanding this breakdown reveals where America sees its most urgent security priorities.
The Navy and Air Force typically command large shares due to costly aircraft, shipbuilding programs, and advanced weapons systems, while the Army focuses heavily on personnel, readiness, and ground modernization. The Marine Corps continues restructuring for rapid-response and Indo-Pacific operations, and the Space Force pushes investment into satellite resilience and space-based defense systems. These allocations signal which domains — land, sea, air, cyber, or space — are receiving strategic emphasis in 2026.
But the real story lies beneath the surface numbers. Within each service’s funding are critical decisions about troop training, maintenance cycles, weapons procurement, and next-generation technology development. As the 2026 budget unfolds, the service-by-service breakdown offers a clear view into how the United States plans to balance present-day readiness with future battlefield dominance.
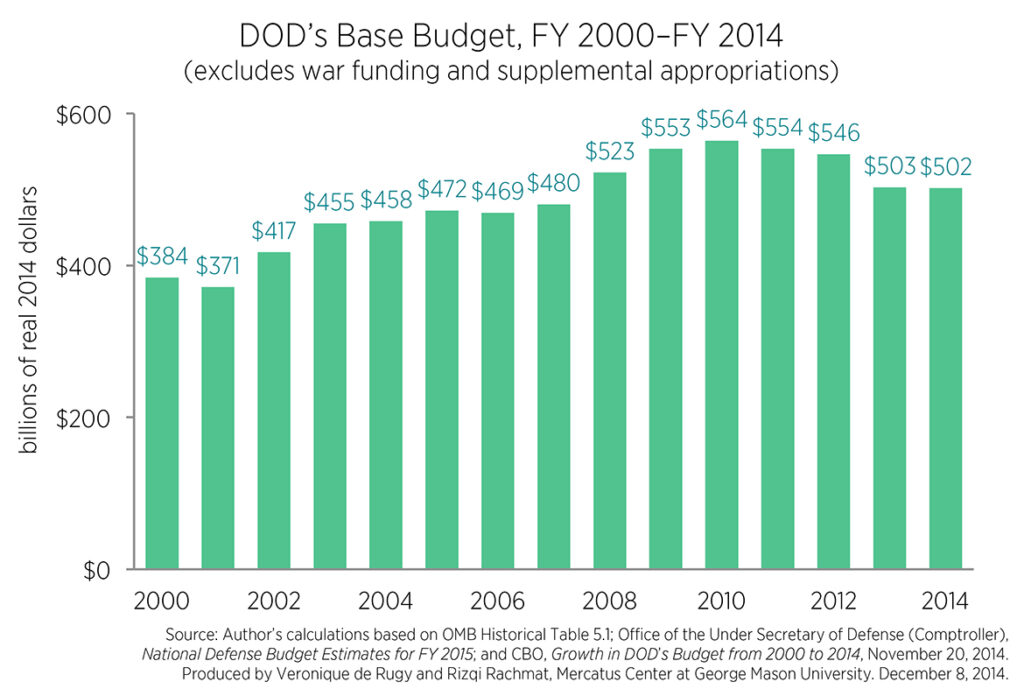
Procurement & R&D in 2026: Who Gets More Funding — F-35 Sustainment, Shipbuilding, or Hypersonics?
Procurement & R&D in 2026: Who Gets More Funding — F-35 Sustainment, Shipbuilding, or Hypersonics?
In the 2026 defense budget, procurement and research & development are where strategy becomes reality. Billions of dollars are set to determine whether the Pentagon prioritizes sustaining existing fleets like the F-35, accelerating naval shipbuilding to counter global rivals, or pushing hypersonic weapons from testing into operational deployment. These choices reveal how the U.S. plans to fight — and win — the next generation of conflicts.
F-35 sustainment funding directly affects aircraft readiness rates, spare parts availability, and long-term lifecycle costs, making it one of the most closely watched line items. Meanwhile, shipbuilding investments shape the size and capability of the U.S. Navy, influencing carrier groups, submarine fleets, and Indo-Pacific presence. Hypersonics, still emerging but strategically critical, represent a race for speed and deterrence dominance in an increasingly competitive global landscape.
The 2026 allocation across these priorities signals whether Washington leans toward maintaining today’s combat power or accelerating tomorrow’s technological edge. With limited fiscal flexibility and rising geopolitical pressure, every dollar in procurement and R&D becomes a strategic bet. The final funding balance will define not just budgets, but battlefield capability for years to come.
Readiness vs. Modernization: Is the 2026 Budget a Rebuild or a Band-Aid?
Readiness vs. Modernization: Is the 2026 Budget a Rebuild or a Band-Aid?
The 2026 defense budget forces a difficult question: should the Pentagon prioritize immediate combat readiness or invest heavily in next-generation modernization? Readiness funding keeps aircraft flying, ships deployable, and troops fully trained today. Modernization funding, on the other hand, prepares the military for tomorrow’s threats — from advanced missile systems to AI-driven warfare.
If more dollars flow into operations and maintenance, the U.S. military strengthens short-term preparedness, ensuring equipment is repaired, munitions are replenished, and training cycles remain uninterrupted. But if modernization dominates, funding accelerates new platforms, space systems, cyber defenses, and emerging technologies designed to deter future adversaries. The tension between these priorities defines whether the 2026 budget stabilizes the force or transforms it.

Ultimately, this isn’t just a financial balancing act — it’s a strategic decision about risk. Investing too heavily in readiness may delay innovation, while focusing too aggressively on modernization could strain current capabilities. The 2026 budget reveals how policymakers are navigating that razor-thin line between rebuilding strength and applying a temporary fix.
The Industrial Base under Pressure: How 2026 Funding Affects Shipyards, Munitions, and Suppliers
The 2026 defense budget does more than fund troops and weapons — it directly shapes the strength of America’s defense industrial base. Shipyards, missile manufacturers, and thousands of suppliers depend on stable, predictable funding to expand capacity and meet rising global demand. When allocations shift, production timelines, workforce hiring, and long-term contracts move with them.

Shipbuilding accounts determine whether naval yards can modernize infrastructure and speed up submarine and carrier construction. Munitions funding affects how quickly stockpiles are replenished and whether factories can scale production lines for artillery shells, missiles, and precision-guided systems. For smaller subcontractors across dozens of states, even minor procurement delays can disrupt supply chains and financial stability.
Under pressure from global security demands and fiscal constraints at home, 2026 funding decisions will test the resilience of the industrial base. Strong investment could strengthen domestic manufacturing and reduce dependency risks, while uncertainty could slow output at a critical moment. The outcome will influence not just defense readiness, but the broader U.S. manufacturing ecosystem for years to come.
Personnel & Pay in 2026: How Much of the Budget Goes to Troops, Benefits, and Recruiting?
In the 2026 defense budget, personnel costs remain one of the largest and most closely watched categories. Billions are allocated to basic pay, housing allowances, healthcare, retirement benefits, and family support programs — expenses that directly affect the lives of service members and their families. These commitments reflect not just military priorities, but a national promise to those who serve.

Beyond compensation, funding for recruiting and retention has become increasingly critical as the armed forces face staffing challenges. Bonuses, education incentives, childcare support, and quality-of-life improvements are now central tools in attracting and keeping skilled personnel. The 2026 allocation reveals whether policymakers believe stronger financial incentives are key to maintaining force strength.
But rising personnel costs also create budgetary tension. As compensation and benefits grow, they consume a larger share of the overall defense budget, potentially limiting funds available for modernization and procurement. How Congress balances these competing priorities in 2026 will shape not only troop morale and readiness, but the long-term structure of the U.S. military itself.
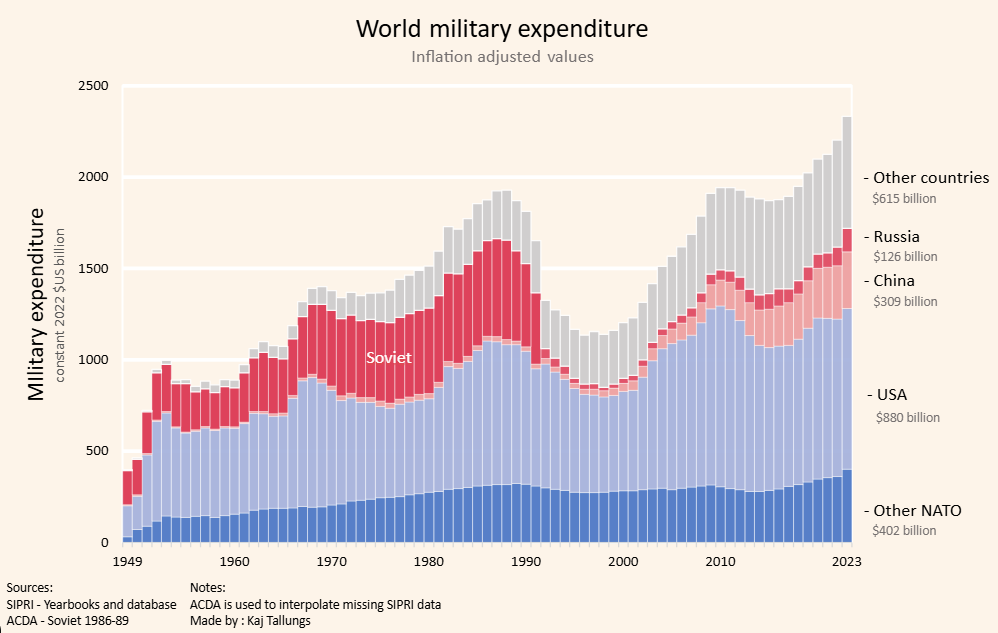
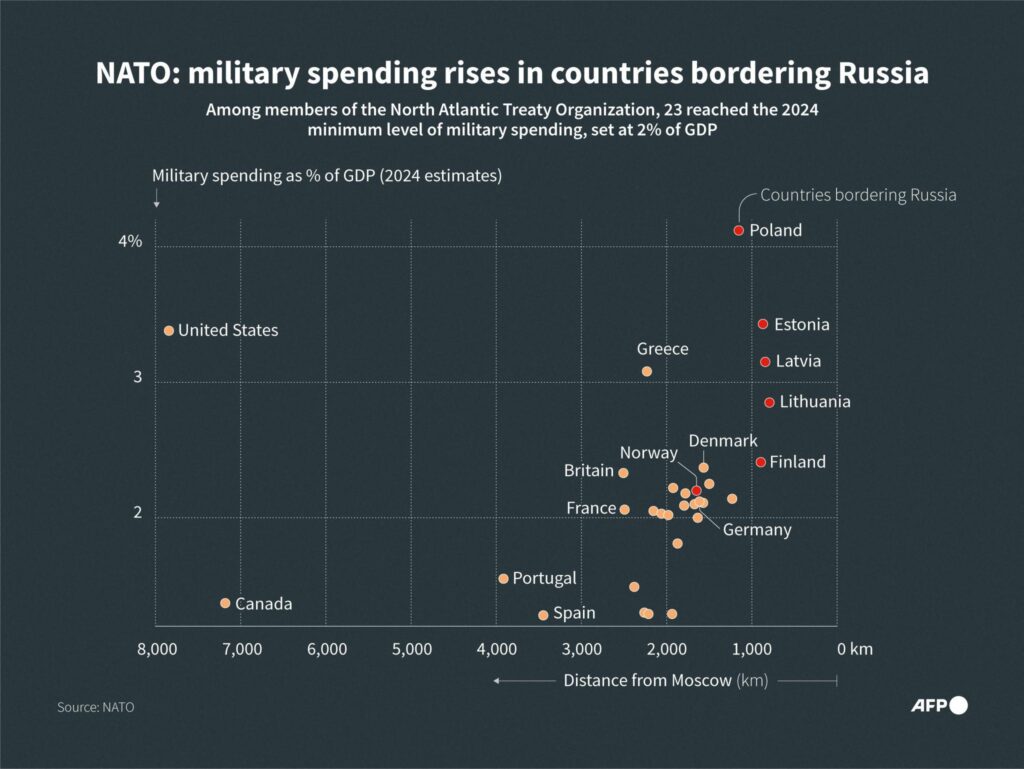
The Global Picture: How U.S. Defense Spending in 2026 Compares to NATO Partners and China
The 2026 U.S. defense budget stands at a level that surpasses the combined military spending of many allied nations, reinforcing America’s position as the world’s largest defense spender. While NATO partners have steadily increased their budgets in response to global tensions, the U.S. still carries a disproportionate share of collective defense costs. This imbalance fuels ongoing debates about burden-sharing and alliance responsibility.
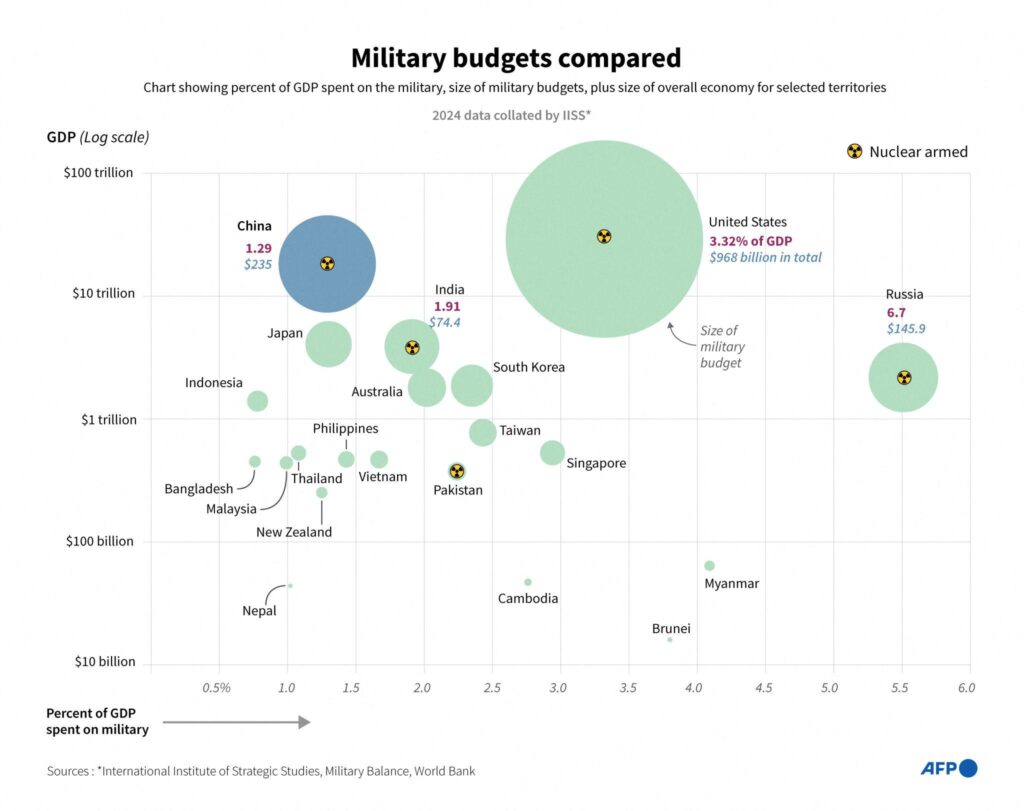
At the same time, comparisons with China draw even sharper attention. Beijing’s officially reported defense spending continues to rise annually, with significant investments in naval expansion, missile systems, and advanced technologies. Although U.S. spending remains higher in absolute terms, China’s rapid growth rate and regional focus create a strategic competition that shapes nearly every Pentagon funding decision.
The 2026 numbers are not just about totals — they reflect priorities, capabilities, and global influence. When measured against NATO allies and China, U.S. spending reveals both unmatched scale and growing strategic pressure. Understanding this global context is essential to grasping why Washington’s budget debates carry consequences far beyond America’s borders.
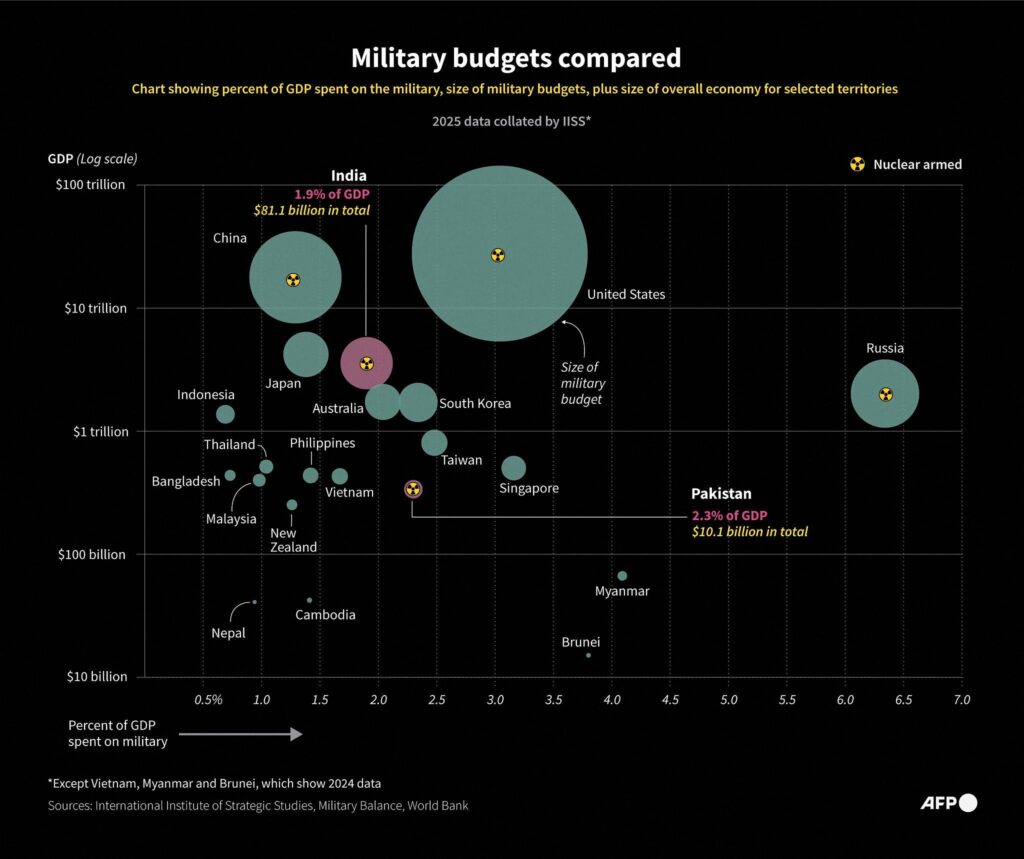
Emergency Requests, Reconciliation, and War Aid: Extra Funding Streams Shaping the 2026 Total
The 2026 defense budget is not defined by its base funding alone — emergency requests, reconciliation measures, and supplemental war aid dramatically influence the final total. These additional streams can add tens of billions of dollars beyond the standard Pentagon request, reshaping how the overall figure is perceived. For readers watching the topline number climb, understanding these add-ons is essential to seeing the full fiscal picture.
Emergency funding is often used to respond quickly to global crises, replenish weapons stockpiles, or support allies during active conflicts. Reconciliation bills, which can move through Congress under special budget rules, sometimes channel defense-related spending outside traditional appropriations debates. Together, these mechanisms create a layered funding structure that goes far beyond the standard annual allocation.
The result is a defense total that reflects both planned strategy and real-time geopolitical pressures. These extra funding streams can accelerate munitions production, support international security commitments, and strengthen U.S. readiness — but they also intensify debates over federal deficits and long-term debt. To truly understand the 2026 defense number, readers must look beyond the base budget and examine the emergency layers shaping America’s global posture.
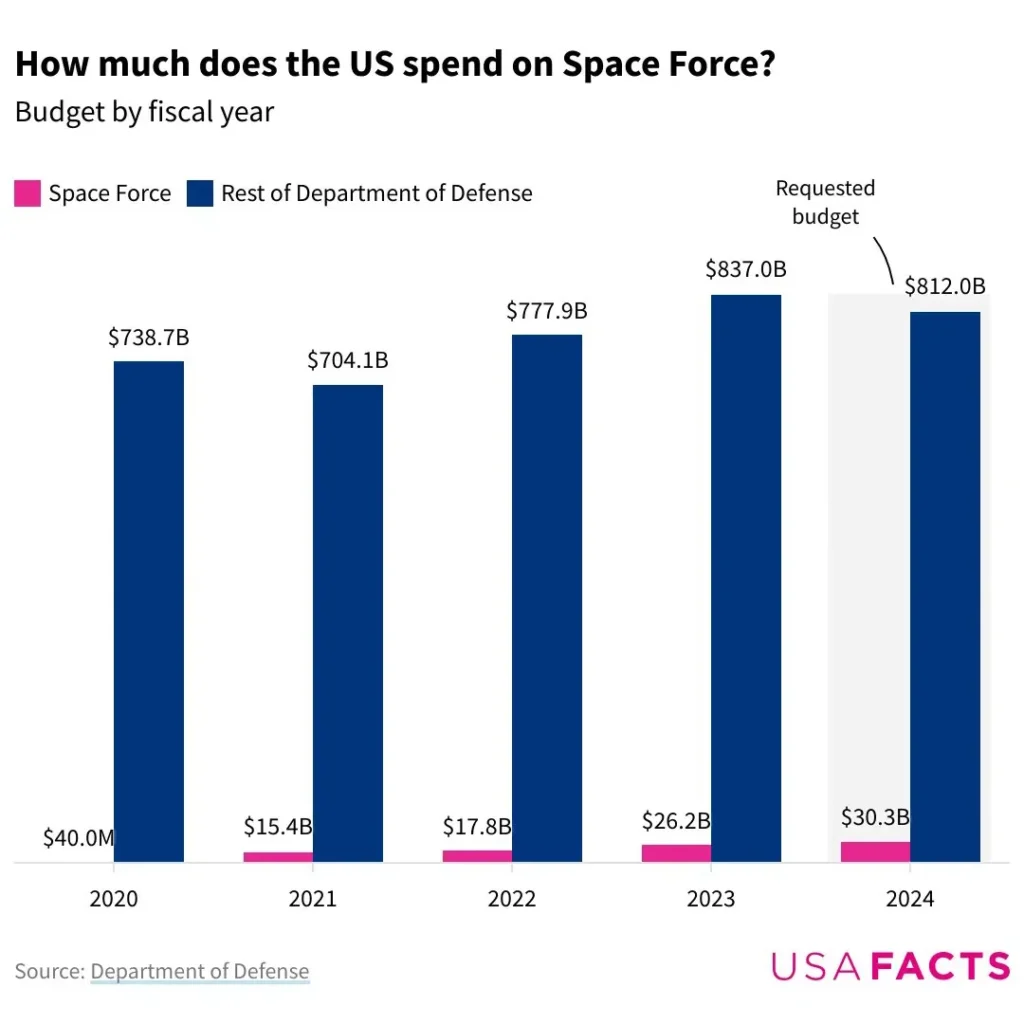
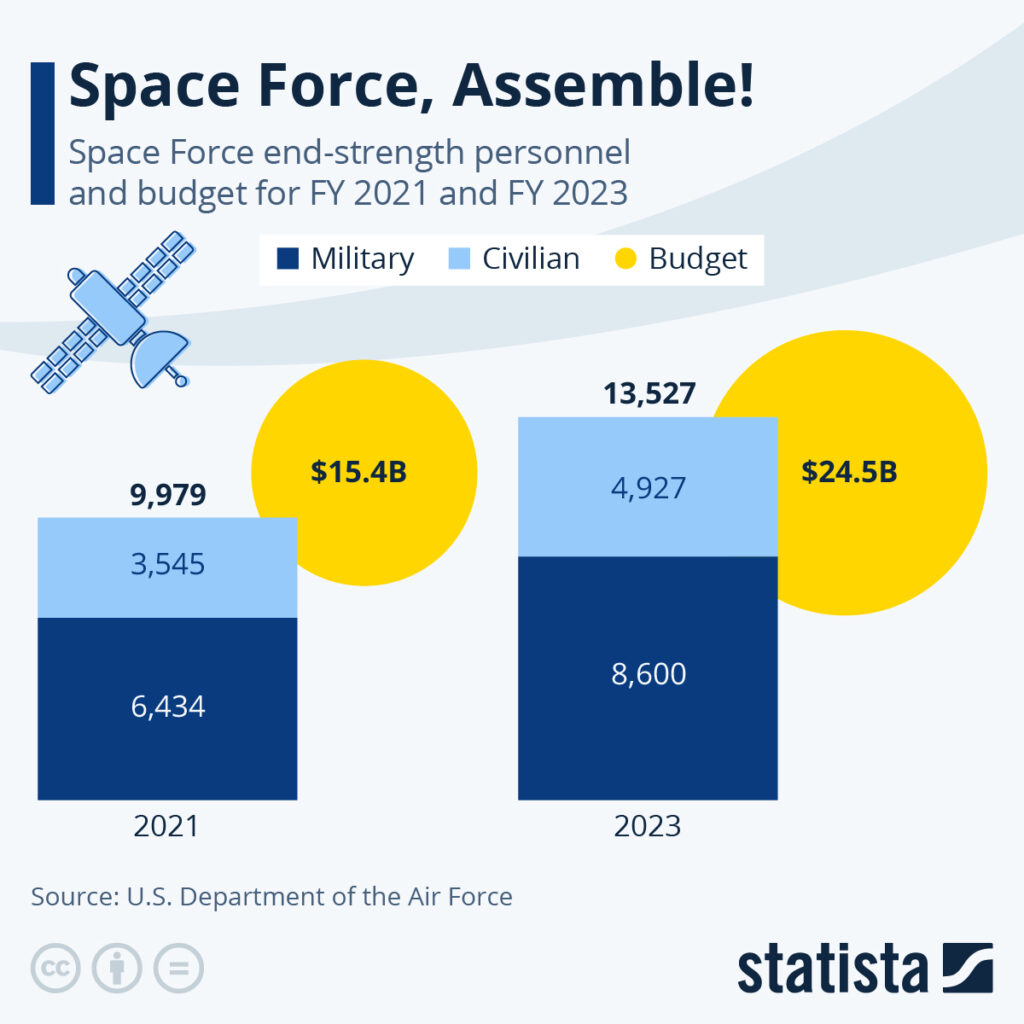
Budgeting for the Future Fight: Space, Cyber, and AI Funding in the FY2026 Request
The FY2026 defense request makes one thing clear: tomorrow’s battlefield will not be defined by tanks alone, but by satellites, algorithms, and invisible networks. Funding for space resilience, cyber defense, and artificial intelligence reflects a strategic pivot toward domains where speed, data, and technological superiority determine advantage. These investments signal how seriously Washington views the risks of digital warfare and orbital vulnerability.
Space funding supports satellite protection, missile-warning systems, and secure communications essential to modern military operations. Cyber allocations strengthen offensive and defensive capabilities designed to counter state-sponsored hacking, infrastructure attacks, and digital espionage. Meanwhile, AI research accelerates autonomous systems, predictive logistics, and real-time battlefield analytics — tools that could redefine decision-making in future conflicts.
The scale and direction of these 2026 investments reveal whether the United States is preparing for the next war, not the last one. As rivals expand their own space and cyber capabilities, falling behind in these arenas could carry strategic consequences far beyond traditional military power. The FY2026 budget offers a glimpse into how America plans to secure technological dominance in an increasingly complex global security landscape.
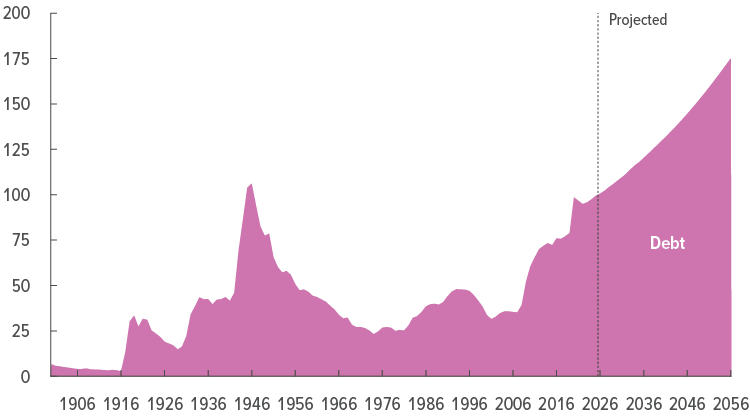
Deficit, Debt, and Defense: Fiscal Risks and Political Pushback to the 2026 Military Budget
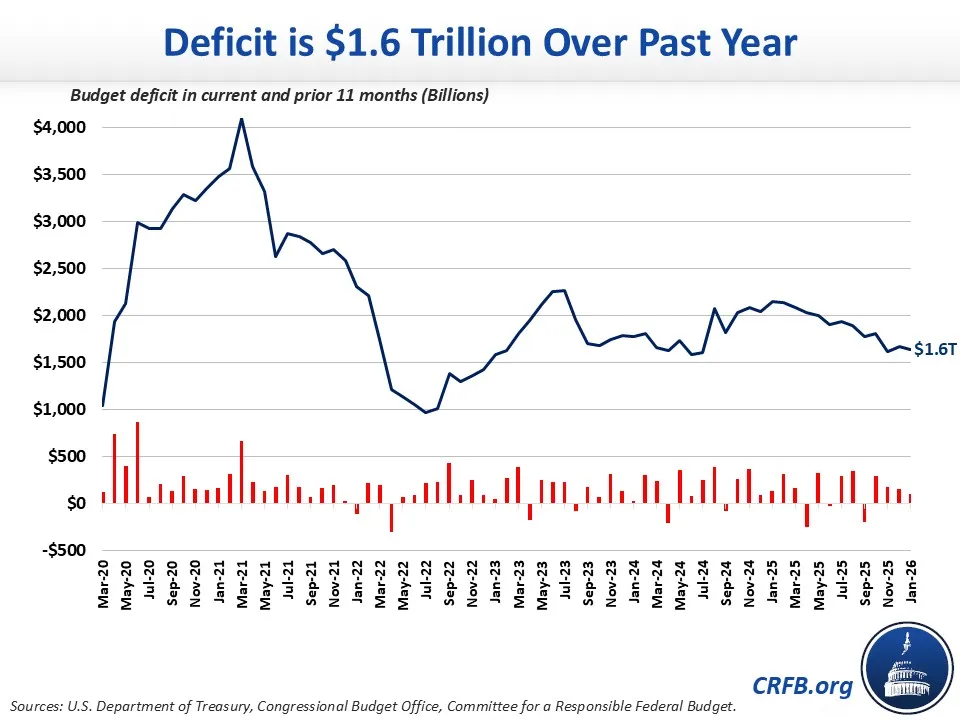
The 2026 military budget arrives at a moment when federal deficits remain elevated, and the national debt continues to climb. As defense spending approaches historic levels, lawmakers and fiscal analysts are asking whether long-term borrowing can sustain such growth. The debate is no longer just about national security — it is about financial stability and economic risk.
Supporters argue that a strong defense posture deters adversaries and protects global trade, making the investment essential despite fiscal strain. Critics counter that rising interest payments on the national debt are consuming a larger share of federal resources, potentially squeezing future defense flexibility. This tension between security priorities and fiscal discipline has fueled sharp political divisions in Washington.
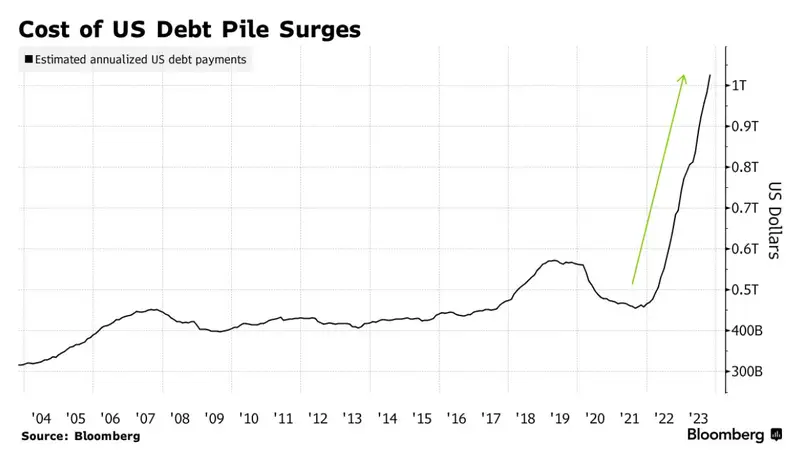
The outcome of this debate will shape not only the size of the 2026 budget but the trajectory of military spending for years to come. If fiscal pressure intensifies, Congress may demand stricter oversight, slower growth, or targeted cuts. Understanding this clash between defense ambitions and debt realities is key to grasping the full stakes behind the 2026 military budget fight.
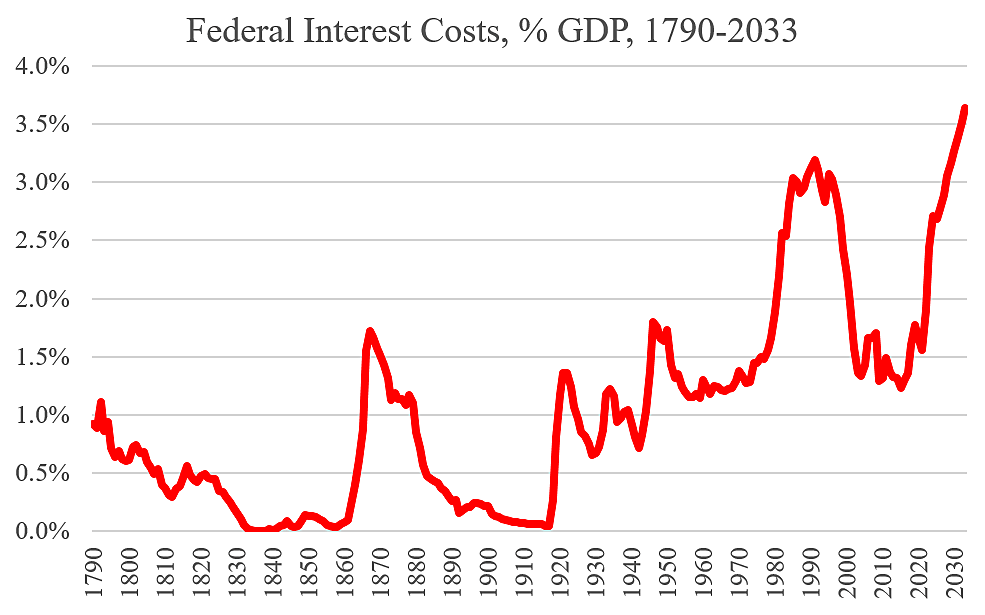
The U.S. defense budget 2026 is more than a spending blueprint — it is a strategic statement about America’s priorities in an uncertain world. From readiness and troop support to modernization, space, cyber, and advanced weapons systems, each dollar reflects choices that will shape military capability for years to come. At the same time, rising deficits and debt levels ensure that every increase faces scrutiny and political resistance.

As Congress finalizes allocations, the real question is not simply how much is spent, but how effectively those funds strengthen national security while maintaining fiscal responsibility. The 2026 debate highlights the delicate balance between deterring global threats and safeguarding long-term economic stability. Ultimately, this budget will influence not only battlefield readiness, but America’s strategic position and financial resilience in the decade ahead.
Subscribe to trusted news sites like USnewsSphere.com for continuous updates.





