A targeted supply chain cyberattack hijacked the official Notepad++ update mechanism, letting suspected Chinese state-linked hackers redirect certain users to malicious software for months in 2025—a serious escalation in the global software supply chain threat landscape that matters now more than ever. This covert campaign exploited infrastructure weaknesses in update delivery, demonstrating how trusted developer tools can become vectors for espionage and compromise critical systems without tampering with source code itself. Experts believe this breach was not random but designed to evade detection and focus on high-value organizations with strategic interests.

What Happened: Hackers Hijacked Notepad++ Updates
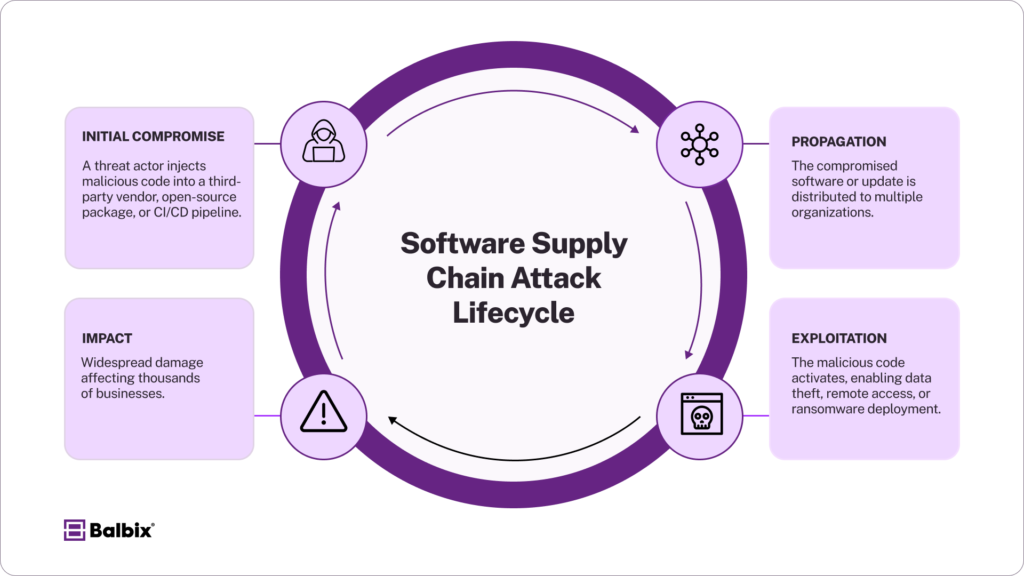
Cybersecurity researchers and the official Notepad++ developer confirmed that from June through December 2025, the update process for Notepad++—a widely used free and open-source text and code editor—was compromised. The attackers gained access to the shared hosting infrastructure supporting Notepad++’s update servers, allowing them to intercept update traffic intended for legitimate users and redirect it to attacker-controlled servers delivering malicious payloads.
The breach did not involve altering Notepad++’s codebase directly; instead, attackers manipulated the broader update ecosystem — a classic supply chain tactic. By exploiting this infrastructure weakness, hackers could selectively target certain users, keeping the majority of the global user base unaffected while avoiding broader detection.
Who Was Targeted and Why
Security analysts report that the campaign was highly selective, focusing on organizations with connections to East Asia, including government, critical infrastructure, and industry sectors where strategic intelligence might be valuable. Victims reportedly experienced what cybersecurity professionals describe as “hands-on” access after installing the compromised updates.
Experts tied the operation to a suspected Chinese state-linked espionage group based on operational behavior, long-running activity patterns, and strategic selection of targets. While direct proof of official state orders remains challenging to confirm without full forensic transparency, the approach aligns with past sophisticated campaigns involving advanced persistent threat (APT) actors.
Why This Matters Now
This incident is significant for software developers, organizations, and national security because it highlights how supply chain vulnerabilities can be exploited at the infrastructure level rather than through flawed application code. Traditional malware defenses often focus on detecting malicious code inside applications—but here, the adversary bypassed those safeguards entirely by abusing a trusted update mechanism.
Supply chain attacks have previously hit major targets like the SolarWinds breach, which compromised U.S. government departments and private sector networks by inserting malware into legitimate updates. That incident, like this one, revealed systemic weaknesses in how software trust is established across complex ecosystems.
How Notepad++ Responded and Mitigations
After detecting the breach, the Notepad++ project took immediate action. It migrated its hosting infrastructure to a provider with stronger security practices and released patched versions of the software (8.8.9 and later) that include enhanced verification of update files and signatures to prevent future redirection attacks.
Developers and users are advised to:
- Install the latest secure version of Notepad++ from the official site.
- Check that update executables are digitally signed and legitimate.
- Monitor for unusual network or system activity related to the update process.
These steps are critical to close gaps that attackers can exploit when trust assumptions break down in the software supply chain.
The Broader Cybersecurity Lesson
The Notepad++ incident reinforces a broader reality: modern software ecosystems are only as secure as the weakest link in their delivery infrastructure. Tools that millions rely on daily — especially open-source ones with decentralized contribution and hosting models — can be manipulated through upstream dependencies if the update path isn’t fortified.
Cyber defenders and organizations should adopt defense-in-depth strategies, which include:
- Rigorous verification of update authenticity (e.g., signed manifests).
- Continuous monitoring of critical infrastructure and dependencies.
- Threat intelligence collaboration to identify suspicious behavior early.
The evolving threat landscape underscores the need for improved industry standards and shared best practices to protect open-source supply chains from being weaponized.
What Users and Organizations Should Do Today
To mitigate exposure from this and similar threats:
- Update immediately to the latest Notepad++ release from official sources.
- Review and audit connected systems for signs of compromise.
- Strengthen update and deployment policies in corporate environments.
Most importantly, this attack serves as a wake-up call about trusting software dissemination infrastructures without robust validation and monitoring.
Subscribe to trusted news sites like USnewsSphere.com for continuous updates.





