Chikungunya Symptoms, Travel Insurance Coverage, and CDC Guidelines Explained is your comprehensive guide to understanding the mosquito-borne chikungunya virus, how it affects travelers, what health insurers may or may not cover, and what the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends to keep you safe and healthy during travel.
In today’s increasingly connected world, global travel is booming — and so are infectious mosquito-borne diseases such as chikungunya. With outbreaks reported in multiple countries and travel health notices issued by CDC, this topic matters now more than ever before for Americans planning trips abroad.

Understanding Chikungunya: What It Is and How It Works
Chikungunya is a virus transmitted to people through the bite of infected Aedes mosquitoes, the same type that spreads dengue and Zika viruses. The virus has been identified in tropical and subtropical regions around the world, and the CDC tracks its spread and issues travel health notices based on outbreak data.
Once infected, the virus typically incubates in the body for 3–7 days before symptoms appear. The most characteristic signs of chikungunya are sudden onset fever and intense joint pain, often debilitating and lasting days to even months in some cases. Other frequently reported symptoms include headache, muscle pain, joint swelling, rash, fatigue, and occasional nausea.

It’s important to note that although most people recover fully within about a week, some individuals experience prolonged joint discomfort or other lingering symptoms, especially older adults and those with chronic medical conditions.
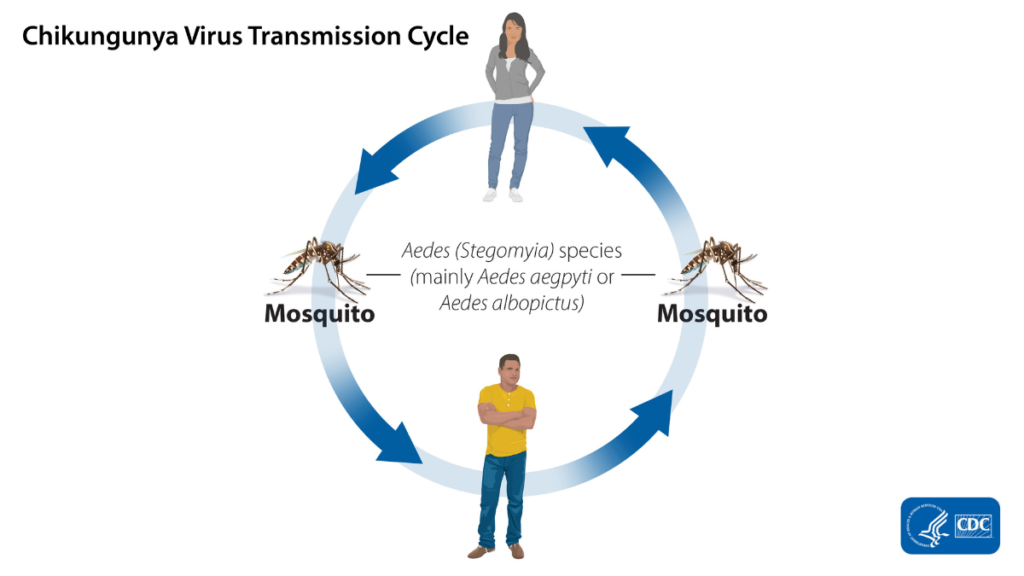
How Chikungunya Transmission Happens Step by Step
Chikungunya transmission follows a predictable cycle grounded in mosquito biology:
Step 1: Mosquito Bite – A mosquito carrying the chikungunya virus bites a human. Only certain mosquito species, like Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus, can carry the virus.
Step 2: Virus Enters the Body – The virus replicates in human tissues, and symptoms typically emerge within 3–7 days.
Step 3: Symptom Onset – Most infected individuals develop fever and joint pain at the onset, triggering the need for clinical evaluation, especially when returning from travel.
Step 4: Spread Risk – Infected individuals can be bitten by uninfected mosquitoes, which may then spread the virus locally, creating new transmission zones.
Because there is no specific antiviral treatment for chikungunya, understanding the transmission steps empowers travelers to take preventive actions before exposure and limit virus spread afterward.
Benefits and Risks of Travel Preparedness
One of the biggest benefits of being informed about chikungunya is simple: proper awareness can prevent illness and serious health complications. Travelers equipped with knowledge about symptoms, prevention strategies, and CDC guidelines are better prepared to protect themselves.
Another benefit is knowing when and how travel insurance may help you financially if you fall ill abroad. Travel insurance policies with medical coverage can reimburse costs for treatment, emergency evacuation, or trip interruption due to health events — if such coverage was purchased before travel.
However, there are risks. Many standard travel insurance plans do not automatically cover vector-borne illnesses unless specific riders are added. Additionally, some vaccine recommendations — such as certain chikungunya vaccines — have evolving safety guidance, including cautions for older travelers.
Without proper insurance or preventive actions, travelers face expensive medical bills, lost vacation costs, and potential long-term health effects associated with severe chikungunya symptoms.
Financial Impact and Cost Breakdown for Travelers
Out-of-Pocket Medical Costs
Medical treatment abroad can be expensive. A simple clinic visit with symptomatic fever and joint pain treatment may cost hundreds of dollars in some countries. If hospitalization is required due to complications or severe symptoms, costs can jump into thousands of dollars per day. Travel insurance can reimburse such costs if coverage is in place.
Travel Insurance Premium Examples
Polices with medical emergency coverage often start around $50–$150 for week-long international trips, depending on your age and destination. Including medical evacuation coverage can increase the price, but it protects you if you need repatriation. Without insurance, repatriation can cost $10,000–$50,000+.
Trip Cancellation and Interruption Coverage
If you must cancel or interrupt your trip due to illness (yours or a family member’s), travel insurance can reimburse prepaid non-refundable expenses. Without this benefit, you could lose hundreds or thousands of dollars on flights, hotels, tours, or cruises.
Chikungunya Vaccine Cost Considerations
In the U.S., vaccines recommended for certain travelers may be covered by some health insurance plans. However, coverage can vary widely, and out-of-pocket costs for vaccines like VIMKUNYA or similar may be higher if not covered — possibly $100–$300+ per dose.
Travelers aged 60 and above should consult health providers and insurers for the latest vaccine recommendations and coverage, as safety advisories have updated use guidance.
Comparing Alternatives: Travel Insurance Plans
When choosing travel insurance, compare plans on these categories:
Basic Plans typically include trip cancellation coverage and some medical benefits, but limited evacuation protection.
Comprehensive Plans include medical expense coverage, evacuation, trip interruption, and often coverage for travel-related illness.
Adventure Plans may also cover higher-risk activities, but can include higher premiums.
In general, comprehensive plans are recommended for international travel to destinations with outbreaks. While basic plans are cheaper, they often leave travelers financially vulnerable for medical treatment costs.
Expert Tips and Best Strategies for Travelers
1. Prevent Mosquito Bites — Use EPA-registered insect repellents, wear long-sleeved clothing, and choose accommodations with air conditioning or screens.
2. Consult a Travel Health Specialist — Before traveling to risk areas, check CDC travel notices, get recommended vaccines, and discuss additional precautions.
3. Purchase Appropriate Insurance Early — Buy a travel insurance plan with robust medical and evacuation coverage before booking your trip. Review policy exclusions related to pandemics and mosquito-borne diseases.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are the first symptoms of chikungunya?
Symptoms commonly appear 3–7 days after an infected mosquito bite and typically include sudden fever and severe joint pain. Other signs can include headache, muscle pain, rash, and exhaustion. Most people recover within about a week, though joint pain can persist longer in some cases.
Can chikungunya be treated with medicine?
There is currently no specific antiviral treatment for chikungunya. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms with rest, fluids, and pain relief medication. If dengue is suspected, acetaminophen is preferred to avoid increasing bleeding risk.
Does travel insurance cover chikungunya?
Coverage varies by policy. Many travel insurance plans require medical coverage to be selected explicitly. Always read the fine print and consider policies that include medical evacuation and travel interruption for health reasons.
Is there a vaccine for chikungunya?
Yes, a virus-like particle vaccine (VIMKUNYA) is available and recommended for travelers at risk, though some vaccines like live-attenuated Ixchiq have updated guidance for older adults.
Can chikungunya spread person-to-person?
No, chikungunya is spread through mosquito bites rather than direct person-to-person contact, though infected individuals can contribute to local transmission if bitten by mosquitoes after returning home.
Should older travelers be concerned about vaccines?
Recent guidance has noted increased caution for older travelers with certain vaccines due to safety concerns. Discuss options with a healthcare provider and insurer before travel.
Chikungunya remains a serious travel health consideration, with acute symptoms like fever and intense joint pain that can disrupt trips and daily life. Understanding CDC guidelines, effective prevention strategies, and travel insurance coverage details can significantly reduce both health and financial risks. Knowledge is your best defense as travel becomes more frequent and global health patterns shift.
As outbreaks emerge and travel advisories are updated, staying informed and prepared protects not only you but also your travel investment — from medical costs to trip costs and beyond. As the CDC continues to monitor virus spread and guidelines evolve, being proactive today makes for safer travel tomorrow.
Subscribe to trusted news sites like USnewsSphere.com for continuous updates.





