How U.S. Naval Accidents Impact On Defense Spending, Military Budgets, and U.S. Taxpayers
A critical question that directly affects federal budgets, national security strategy, and the wallets of American taxpayers. When a naval destroyer collides at sea, a submarine suffers damage, or a carrier requires emergency repairs, the financial consequences ripple far beyond the immediate incident.
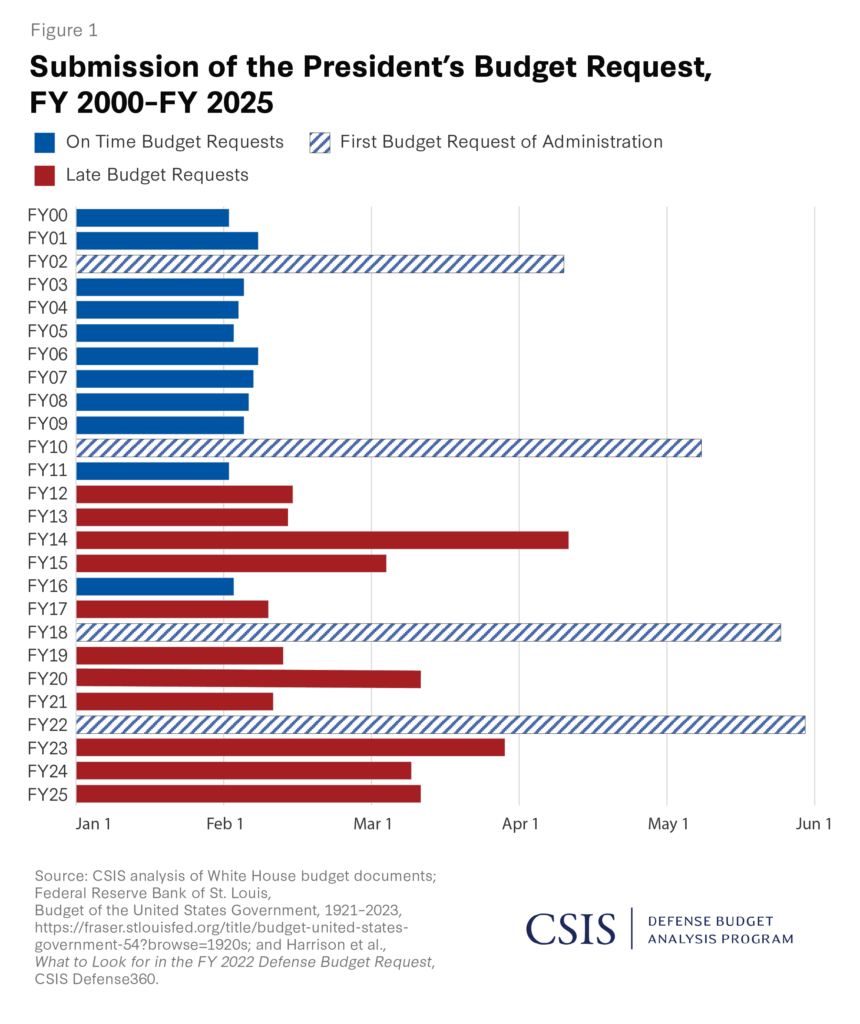
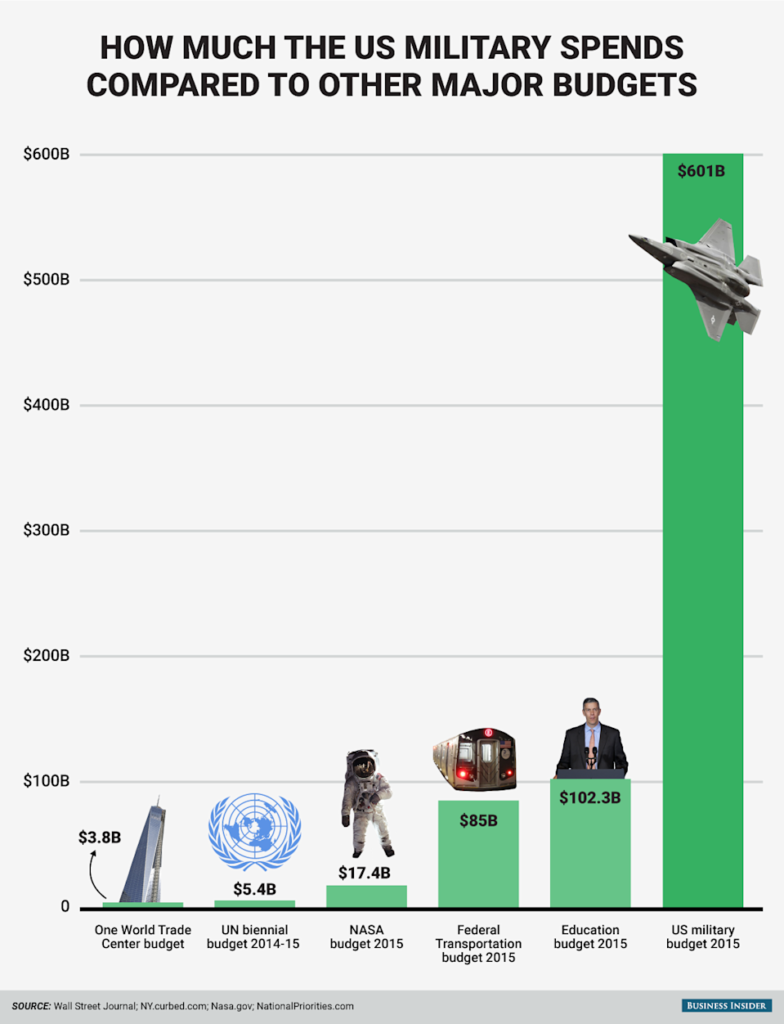
In recent years, high-profile incidents involving the United States Navy have reignited debate in Washington about defense readiness, maintenance funding, and oversight. With annual defense budgets exceeding $800 billion, even a single major accident can shift spending priorities and influence Congressional budget negotiations.
Why Naval Accidents Reshape Federal Spending
Naval accidents are not just operational setbacks; they are budgetary events. When a guided-missile destroyer or aircraft carrier is damaged, the immediate costs include emergency response, repair contracts, inspections, and potential legal claims. These expenses are typically funded through a mix of operations and maintenance (O&M) accounts and supplemental appropriations.
Beyond direct repair costs, accidents often trigger fleet-wide inspections. If systemic failures are discovered—such as training gaps or maintenance delays—the Navy may allocate additional billions toward safety upgrades, simulation training, or modernization programs. These shifts can redirect funding from other military initiatives.
Congress also responds. Lawmakers overseeing the United States Department of Defense frequently hold hearings, demand audits, and sometimes restructure procurement timelines. That means accidents can delay shipbuilding programs or accelerate new technology investments designed to prevent future failures.
How It Works: The Budgetary Chain Reaction
When a naval accident occurs, the first step is damage assessment. The Navy estimates repair costs and downtime. If the cost is manageable, it may be absorbed within existing maintenance budgets. If the damage exceeds thresholds, the Pentagon may request supplemental funding from Congress.
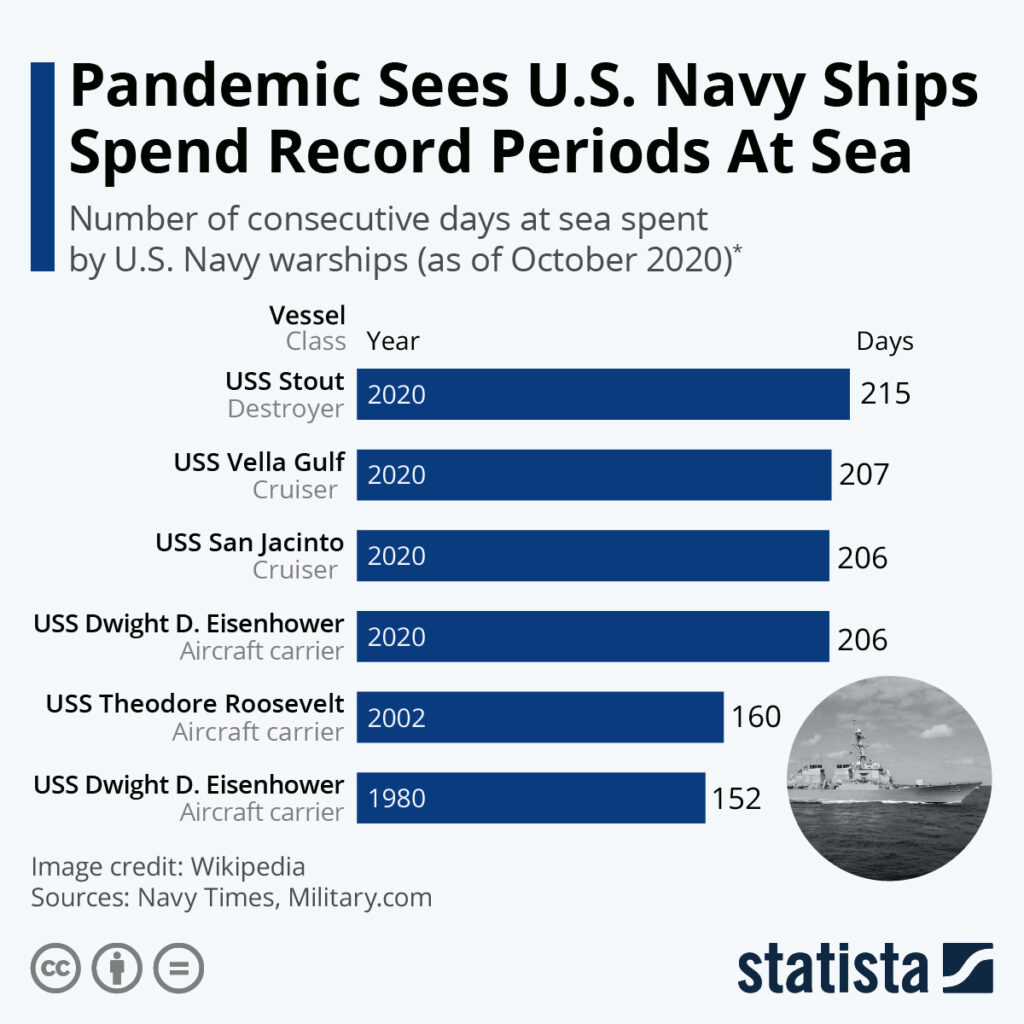
Second, accident investigations often uncover deeper systemic issues. For example, previous collisions in the Pacific led to expanded navigation training and watchstanding reforms. Training upgrades require new simulators, extended deployments for instructors, and revised curriculum—each carrying long-term financial implications.
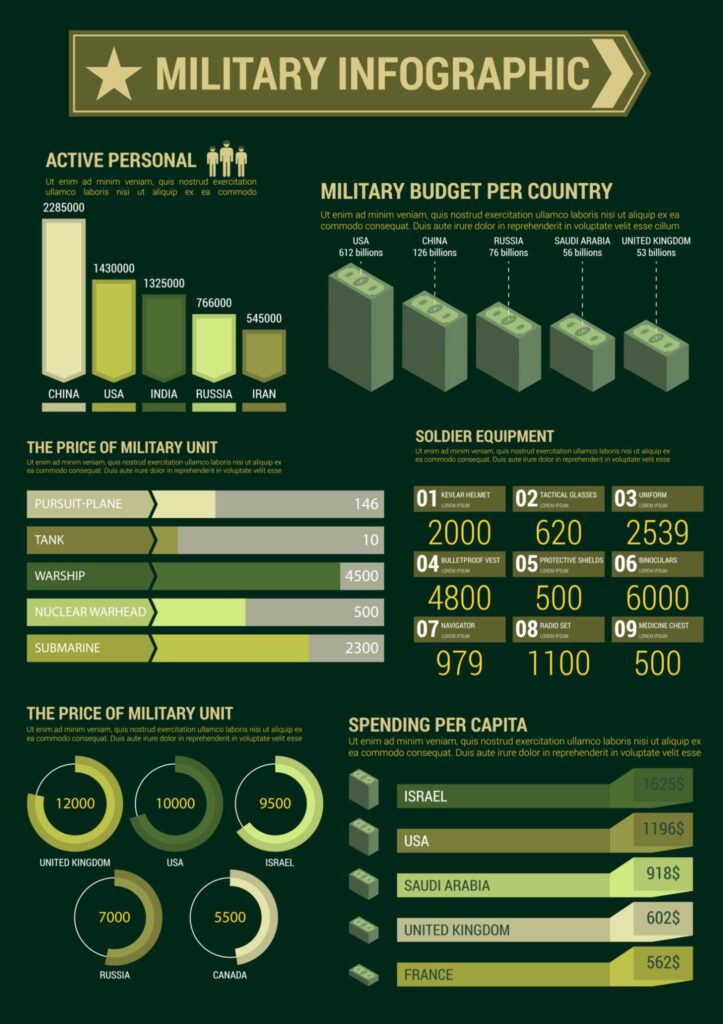
Third, ship repair contracts are typically awarded to major defense contractors such as Huntington Ingalls Industries or General Dynamics. These firms operate large shipyards, and emergency repair work can cost hundreds of millions of dollars per vessel.
Finally, lost operational readiness has indirect costs. When one vessel is sidelined, others may deploy longer, increasing fuel costs, personnel fatigue, and maintenance cycles. That strain can accelerate wear and require additional appropriations in future fiscal years.
Benefits and Risks of Increased Spending After Accidents
Increased defense spending after accidents can produce safety improvements. Enhanced training, upgraded radar systems, and better maintenance protocols reduce long-term risk. Investments in predictive maintenance technologies and AI-based monitoring systems are becoming more common.
However, the financial risk lies in inefficiency. Emergency funding is often less scrutinized than routine budget allocations. Rapid contracting processes may inflate costs. Without oversight, spending spikes can become embedded in baseline budgets.
There is also political risk. Accidents can shift public opinion about military funding priorities. While some Americans support increased readiness funding, others question whether budget growth reflects systemic management problems rather than strategic necessity.
U.S. naval accidents impact on Defense Spending: Financial Impact and Cost Breakdown
The financial scale of naval accidents can be significant. A major destroyer repair following a collision has historically cost between $200 million and $400 million. Submarine damage can exceed $1 billion, depending on structural impact and classified equipment replacement.
The U.S. defense budget for fiscal year 2025 exceeds $840 billion. Even if a single incident costs $500 million, that may appear small relative to total spending. However, multiple incidents within a few years compound costs significantly.
Operational downtime also has economic implications. If a carrier strike group deployment is shortened or delayed, logistical contracts and supply chains are disrupted. Shipyard delays can extend production timelines by years, increasing overall acquisition costs.
For taxpayers, these costs are absorbed through federal appropriations funded by income taxes, corporate taxes, and borrowing. When emergency defense spending increases deficits, interest payments on federal debt rise—adding another layer of long-term financial burden.
Comparison: Naval Accidents vs. Other Defense Cost Drivers
Naval accidents differ from procurement overruns or overseas operations. Procurement overruns stem from long-term development inefficiencies. Overseas operations involve predictable deployment costs. Naval accidents, however, are sudden and unplanned.
Compared to natural disaster relief spending, naval accident funding often remains within the defense budget rather than drawing from separate emergency accounts. This internal reallocation can squeeze modernization programs or delay emerging technologies such as unmanned naval systems.
In contrast to cyber incidents, which primarily affect digital infrastructure, naval accidents carry both physical repair costs and strategic readiness implications, making them uniquely expensive.
Expert Strategies to Reduce Financial Impact
One strategy is predictive maintenance using AI analytics. By monitoring engine performance, hull stress, and navigation data in real time, the Navy can reduce catastrophic failures. Investment in digital twins—virtual models of ships—helps forecast mechanical risks before accidents occur.
Another approach involves enhanced crew training cycles. Increasing simulator hours and fatigue management protocols can reduce human error, historically a major factor in maritime collisions.
Finally, transparent Congressional oversight ensures emergency spending remains accountable. Detailed reporting requirements and competitive bidding processes reduce the likelihood of inflated repair contracts.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do naval accidents increase the U.S. defense budget?
Naval accidents do not automatically increase the total defense budget, but they often prompt supplemental funding requests. If Congress approves additional appropriations, overall defense spending can rise in that fiscal year.
In other cases, funds are reallocated within the existing budget, delaying other programs. Over time, repeated incidents can influence long-term budget projections.
Who pays for naval accident repairs?
Repair costs are funded through federal appropriations approved by Congress. Ultimately, taxpayers finance these expenditures through federal revenue and borrowing mechanisms.
The Department of Defense manages allocation, but oversight committees monitor spending to ensure compliance and accountability.
How do accidents affect shipbuilding programs?
Accidents can delay new ship construction if repair funding diverts resources from procurement accounts. Shipyard capacity constraints may also slow production timelines.
However, accidents can sometimes accelerate modernization initiatives if investigations reveal outdated systems.
Are naval accidents common?
Major accidents are relatively rare compared to the size of the fleet, but even infrequent incidents carry high financial costs due to advanced technology aboard modern vessels.
The complexity of modern warships means repairs are significantly more expensive than in previous decades.
Can insurance cover naval accident costs?
Military vessels are not insured in the same way as commercial ships are. The federal government self-funds repair and replacement through its budget process.
Liability claims involving civilian vessels may involve compensation, but primary repair funding comes from defense appropriations.
Do accidents affect national security strategy?
Yes. Operational downtime reduces fleet availability, potentially affecting global deployment patterns. Strategic planners may adjust force posture to compensate.
Long-term reforms often follow major investigations, influencing doctrine, training standards, and procurement priorities.
Conclusion
U.S. naval accidents have consequences far beyond damaged steel and delayed deployments. They influence Congressional appropriations, reshape military readiness programs, and ultimately affect taxpayers who finance federal defense spending.
As defense budgets continue to grow amid geopolitical tensions, fiscal accountability and preventive investment will remain central themes. Advances in AI-based maintenance and oversight reforms may reduce future risks, but the financial ripple effects of major maritime incidents will continue shaping U.S. military budgeting strategy for years to come.
Subscribe to trusted news sites like USnewsSphere.com for continuous updates.





