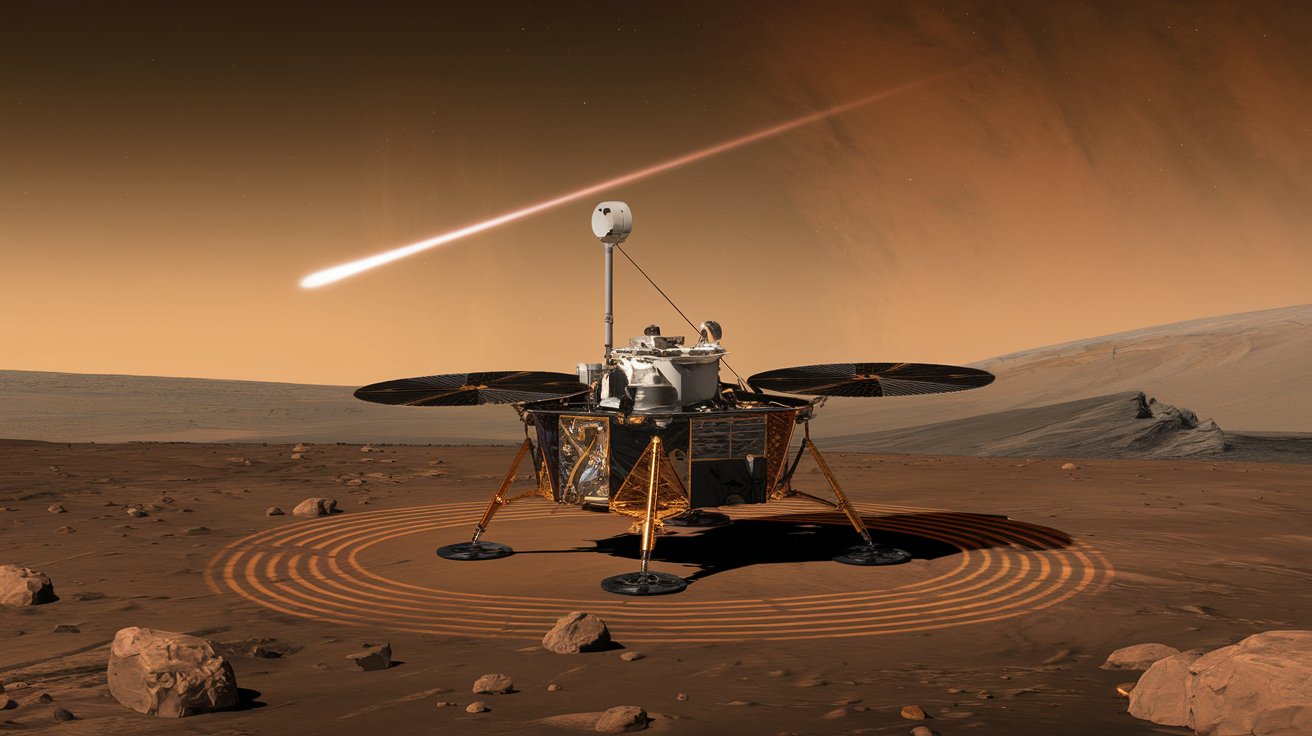
NASA’s InSight Discovers Unexpected Depth of Marsquakes
NASA’s InSight mission has unearthed groundbreaking discoveries about seismic activity on Mars, particularly in relation to marsquakes triggered by meteoroids. The findings challenge our understanding of the Martian interior and open new avenues for research. In this article, we will dive into the details of these revelations, the implications for future Mars exploration, and what we can learn from this cutting-edge research.
Table of Contents
The InSight Mission: A Brief Overview
The InSight (Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport) lander was deployed on the Martian surface in November 2018. Its primary objective is to study the planet’s interior structure, providing vital information about its geology and formation.
- Mission Goals:
- Understand the geophysical characteristics of Mars
- Identify the sources and frequency of marsquakes
- Analyze the Martian crust, mantle, and core
Unpacking the Discovery of Marsquakes
InSight’s seismometer has detected over 1,300 seismic events to date. Among them, a significant portion is attributed to meteoroids colliding with Mars, sending shockwaves through the planet’s crust. Previous models suggested these disturbances would cause only shallow marsquakes, but the recent findings indicate that:
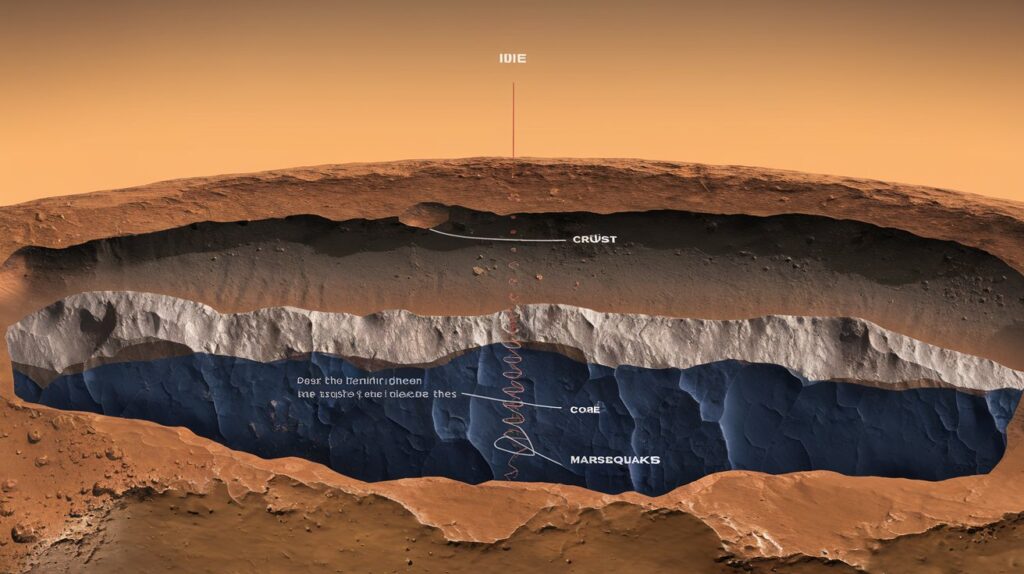
- The marsquakes caused by meteoroid impacts can penetrate much deeper into the Martian crust than expected.
- Some of these events have reverberated through the planet, producing seismic signals detectable by the InSight lander.
What Makes Marsquakes Different?
Understanding the nature of marsquakes is crucial for grasping the geological processes at work on Mars. Marsquakes differ from Earthquakes in several ways:
- Magnitude and Frequency: Earth experiences frequent quakes due to tectonic activity. Marsquakes, however, are less frequent and tend to be less energetic.
- Origin: While most Earthquakes stem from tectonic shifts, many marsquakes originate from meteoroid impacts, showcasing Mars’ fragile crust.
- Resonance: The deeper penetration of marsquakes changes the way seismic waves resonate, making the seismic analysis different from terrestrial models.
Significance of the Findings
The discovery that marsquakes can originate from significant depths has far-reaching implications for our understanding of Mars:
- Revealing the Martian Interior: The depth of the seismic activity indicates a more complex interior than previously believed. Understanding these depths can enhance our knowledge of planet formation and evolution, not just on Mars, but for terrestrial planets in general.
- Aiding Future Missions: Insights gained from these marsquakes can help in planning future missions. Knowing the geological and seismic nature of Mars will assist in selecting landing sites and designing habitats for potential human exploration.
- Comparative Planetology: The study of marsquakes can bring about insights when compared with seismic activity on the Moon and other celestial bodies, allowing scientists to make broad conclusions about planetary formations.
How InSight Operates
InSight is equipped with a suite of scientific instruments designed to measure seismic activity, thermal properties, and atmospheric pressure. Key components include:
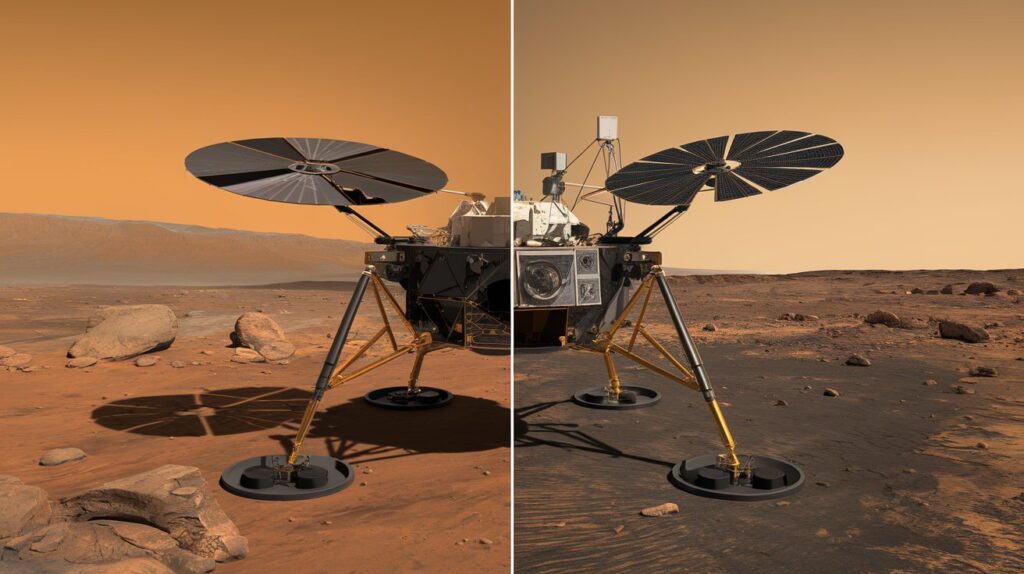

- SEIS (Seismic Experiment for Interior Structure): This sensitive seismometer captures seismic waves and records their speed and intensity.
- HP3 (Heat Flow and Physical Properties Package): This instrument burrows into the Martian soil to measure heat flow, providing additional context for the seismic data.
- APSS (Atmospheric Pressure Sensors): These sensors monitor Martian weather and atmospheric conditions, which may influence seismic activity.
The Ongoing Exploration of Mars
The discoveries made by InSight contribute to our ever-growing understanding of Mars. Future missions, including potential human landings, will benefit from the geological and seismic insights provided by InSight’s findings.
- International Collaboration: NASA collaborates with European and other global space agencies to leverage data and enhance scientific outreach.
- Technological Advancements: The technologies developed for InSight and future missions may lead to innovations in seismology on Earth.
- Public Engagement: Sharing these discoveries with the public is vital. NASA aims to inspire the next generation of scientists and engineers through educational outreach programs.
Conclusion
The InSight mission has transformed our understanding of Mars and its seismic activity. The revelations about the depth of marsquakes caused by meteoroids provide valuable insights into the planet’s inner workings. As we continue to study these seismic signals, we uncover the hidden dynamics of the Red Planet and pave the way for future exploration.
As research continues, we envision a future where we can understand not only Mars’s past but also its potential for supporting human life, making the dreams of Martian colonization a step closer to reality. [USnewsSphere.com]