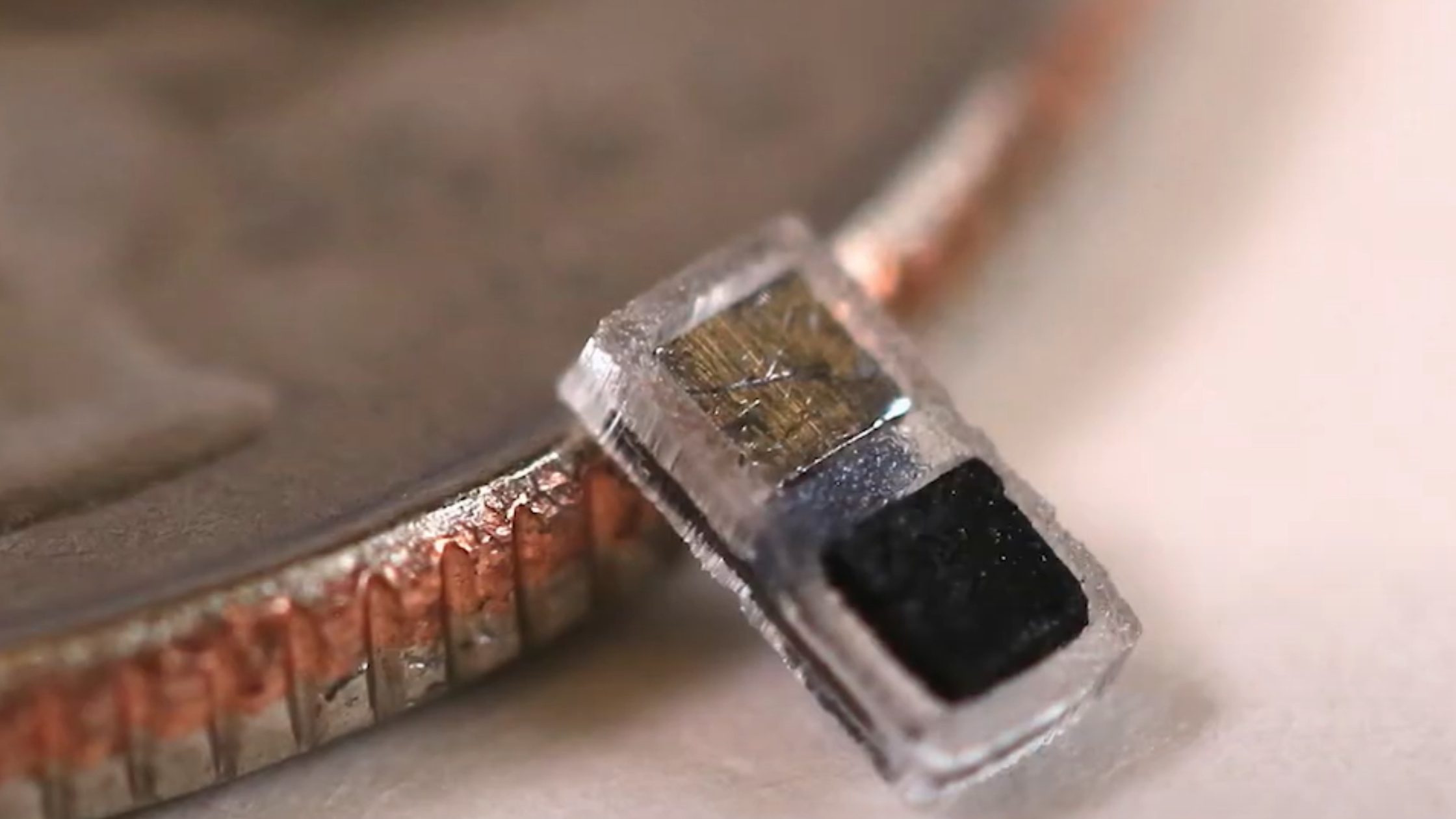
Biodegradable Pacemaker Breakthrough: Northwestern University Unveils the World’s Smallest Life-Saving Heart Device — A revolutionary development in pediatric healthcare, this device is set to transform the way newborns are treated after heart surgery across the United States.
What Is a Biodegradable Pacemaker and Why Does It Matter?
This innovative pacemaker is a tiny, rice-sized device that provides temporary cardiac support to newborns after surgery. Unlike traditional pacemakers, it dissolves safely in the body, eliminating the need for removal surgery.
Key Features:
- Size: 3.5mm x 1.8mm
- Powered by bodily fluids (galvanic cell)
- Wire-free, battery-free, and surgery-free for removal
- Targets post-surgical arrhythmias in infants

How This Wireless Pacemaker Works (Step-by-Step)
A soft, skin-worn patch sits on the baby’s chest and monitors heart rhythms. If it detects irregularities, it sends light pulses through the skin, activating the pacemaker inside. The light triggers electrical signals to stabilize the heartbeat.
Flow of Operation:
- Wearable detects heartbeat irregularity
- Light signal activates implanted device
- Pacemaker sends electrical pulse to heart
- Device dissolves naturally in 5–7 days
Traditional Pacemaker vs Biodegradable Pacemaker
| Feature | Traditional Pacemaker | Biodegradable Pacemaker |
|---|---|---|
| Size | About a matchbox | Smaller than a grain of rice |
| Implantation | Requires invasive surgery | Injected with a syringe |
| Removal | Needs second surgery | Dissolves in body |
| Power Source | Batteries and wires | Bodily fluids (chemical reaction) |
| Risk Level | Higher (infection, bleeding) | Minimal (non-invasive, no wires) |
| Suitability for Newborns | Difficult due to size and risk | Designed specifically for infants |
Biodegradable Pacemaker at a Glance
[ Biodegradable Pacemaker ]
|
-------------------------------------------------
| | |
[ Development ] [ How It Works ] [ Medical Impact ]
- Northwestern U - Wearable patch - Treats arrhythmias
- Pediatric focus - Light activation - For newborns post-surgery
- FDA trials underway - No wires or batteries - Reduces complications
- Dissolves naturally - Future adult use
Why Newborns Benefit Most From This Invention
Each year, over 40,000 babies in the U.S. are born with congenital heart defects. After surgery, many face irregular heartbeats requiring temporary pacing. Traditional devices are too large and often cause complications.
This new solution:
- Offers zero-stress removal
- Reduces infection and internal bleeding risks
- Is tailored for delicate neonatal anatomy
- Is expected to lower hospital stay time and costs
Future Possibilities: Adult Applications & Medical Expansion
Though designed for newborns, researchers plan to scale this for adults requiring temporary pacing, such as after heart attacks or surgeries. Future versions may include:
- Multiple synchronized devices
- Customized pacing regions
- Broader use in nerve and muscle stimulation
Conclusion: A Tiny Device with Life-Saving Potential
Northwestern University’s biodegradable pacemaker is more than a medical invention—it’s a breakthrough that could reshape how heart problems are treated in the most vulnerable patients. By reducing the risks and burdens of current devices, this tiny innovation could soon become a standard of care in U.S. neonatal units, offering safer healing, fewer surgeries, and better outcomes
[USnewsSphere.com / nw]